Dopamine receptor agonists modulate voluntary alcohol intake independently of individual levels of alcohol intake in rats
- PMID: 27236784
- PMCID: PMC4917576
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-016-4330-x
Dopamine receptor agonists modulate voluntary alcohol intake independently of individual levels of alcohol intake in rats
Abstract
Rationale: Individual susceptibility to alcohol use disorder has been related to functional changes in dopaminergic neurotransmission.
Objectives: The aim of the current work was to assess the effects of selective dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists on alcohol consumption in rats that differ in individual levels of alcohol intake.
Methods: The effects of the dopamine D1 receptor agonist SKF 82958, the dopamine D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390, the dopamine D2 receptor agonist sumanirole and the dopamine D2 receptor antagonist L741,626 on alcohol consumption and preference were assessed at different time points after treatment in subgroups of low and high alcohol drinking rats (LD and HD) using an intermittent alcohol access paradigm.
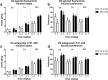
Results: SKF 82958 decreased alcohol intake and alcohol preference throughout the 24-h session. Sumanirole decreased alcohol intake during the first 2 h, but increased alcohol intake during the remainder of the session. The effects of SKF 82958 and sumanirole on alcohol intake and alcohol preference were comparable in LD and HD. By contrast, the dopamine receptor antagonists SCH 23390 and L741,626 did not alter alcohol consumption in either group at any time point.
Conclusions: These data indicate that stimulation of dopamine D1 receptors reduces alcohol intake, but that endogenous dopamine does not play a primary role in alcohol consumption. Moreover, the difference in alcohol consumption between LD and HD does not involve altered dopamine signaling.
Keywords: Addiction; Alcohol; Dopamine receptor; Individual differences.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Barrett AC, Miller JR, Dohrmann JM, Caine SB. Effects of dopamine indirect agonists and selective D1-like and D2-like agonists and antagonists on cocaine self-administration and food maintained responding in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2004;47(Suppl 1):256–273. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

