Loss-of-Function Mutations in FRRS1L Lead to an Epileptic-Dyskinetic Encephalopathy
- PMID: 27236917
- PMCID: PMC4908178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.04.008
Loss-of-Function Mutations in FRRS1L Lead to an Epileptic-Dyskinetic Encephalopathy
Abstract
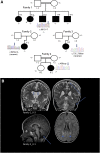
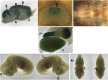
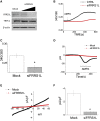
Glutamatergic neurotransmission governs excitatory signaling in the mammalian brain, and abnormalities of glutamate signaling have been shown to contribute to both epilepsy and hyperkinetic movement disorders. The etiology of many severe childhood movement disorders and epilepsies remains uncharacterized. We describe a neurological disorder with epilepsy and prominent choreoathetosis caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in FRRS1L, which encodes an AMPA receptor outer-core protein. Loss of FRRS1L function attenuates AMPA-mediated currents, implicating chronic abnormalities of glutamatergic neurotransmission in this monogenic neurological disease of childhood.
Copyright © 2016 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Guerrini R., Moro F., Kato M., Barkovich A.J., Shiihara T., McShane M.A., Hurst J., Loi M., Tohyama J., Norci V. Expansion of the first PolyA tract of ARX causes infantile spasms and status dystonicus. Neurology. 2007;69:427–433. - PubMed
-
- Gardella E., Becker F., Møller R.S., Schubert J., Lemke J.R., Larsen L.H., Eiberg H., Nothnagel M., Thiele H., Altmüller J. Benign infantile seizures and paroxysmal dyskinesia caused by an SCN8A mutation. Ann. Neurol. 2016;79:428–436. - PubMed
-
- Deprez L., Weckhuysen S., Holmgren P., Suls A., Van Dyck T., Goossens D., Del-Favero J., Jansen A., Verhaert K., Lagae L. Clinical spectrum of early-onset epileptic encephalopathies associated with STXBP1 mutations. Neurology. 2010;75:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Cellini E., Vignoli A., Pisano T., Falchi M., Molinaro A., Accorsi P., Bontacchio A., Pinelli L., Giordano L., Guerrini R., FOXG1 Syndrome Study Group The hyperkinetic movement disorder of FOXG1-related epileptic-dyskinetic encephalopathy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016;58:93–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G108/638/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U142684173/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U42 OD011174/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J004758/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 2014112/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- MC_UP_1502/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DE017102/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A390_1106/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 DE024300/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS083739/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0802760/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 HG006348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

