Immunological Consequences of Intestinal Fungal Dysbiosis
- PMID: 27237365
- PMCID: PMC4900921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.05.003
Immunological Consequences of Intestinal Fungal Dysbiosis
Abstract
Compared to bacteria, the role of fungi within the intestinal microbiota is poorly understood. In this study we investigated whether the presence of a "healthy" fungal community in the gut is important for modulating immune function. Prolonged oral treatment of mice with antifungal drugs resulted in increased disease severity in acute and chronic models of colitis, and also exacerbated the development of allergic airway disease. Microbiota profiling revealed restructuring of fungal and bacterial communities. Specifically, representation of Candida spp. was reduced, while Aspergillus, Wallemia, and Epicoccum spp. were increased. Oral supplementation with a mixture of three fungi found to expand during antifungal treatment (Aspergillus amstelodami, Epicoccum nigrum, and Wallemia sebi) was sufficient to recapitulate the exacerbating effects of antifungal drugs on allergic airway disease. Taken together, these results indicate that disruption of commensal fungal populations can influence local and peripheral immune responses and enhance relevant disease states.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

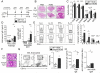
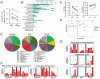
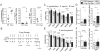
Comment in
-
The Fungal Mycobiota: Small Numbers, Large Impacts.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Jun 8;19(6):750-1. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.05.018. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 27281565
References
-
- Bukelskiene V, Baltriukiene D, Repeckiene J. Study of health risks associated with Aspergillus amstelodami and its mycotoxic effects. Ekologija. 2006;3:42–47.
-
- Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012;10:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Denning DW, O'Driscoll BR, Hogaboam CM, Bowyer P, Niven RM. The link between fungi and severe asthma: a summary of the evidence. Eur. Respir. J. 2006;27:615–626. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

