Molecular Classification of Medulloblastoma
- PMID: 27238212
- PMCID: PMC5221779
- DOI: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0016
Molecular Classification of Medulloblastoma
Abstract
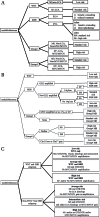
Medulloblastoma (MB) is one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children. The current standard treatment regimen consists of surgical resection, craniospinal irradiation, and adjuvant chemotherapy. Although these treatments have the potential to increase the survival of 70-80% of patients with MB, they are also associated with serious treatment-induced morbidity. The current risk stratification of MB is based on clinical factors, including age at presentation, metastatic status, and the presence of residual tumor following resection. In addition, recent genomic studies indicate that MB consists of at least four distinct molecular subgroups: WNT, sonic hedgehog (SHH), Group 3, and Group 4. WNT and SHH MBs are characterized by aberrations in the WNT and SHH signaling pathways, respectively. WNT MB has the best prognosis compared to the other MBs, while SHH MB has an intermediate prognosis. The underlying signaling pathways associated with Group 3 and 4 MBs have not been identified. Group 3 MB is frequently associated with metastasis, resulting in a poor prognosis, while Group 4 is sometimes associated with metastasis and has an intermediate prognosis. Group 4 is the most frequent MB and represents 35% of all MBs. These findings suggest that MB is a heterogeneous disease, and that MB subgroups have distinct molecular, demographic, and clinical characteristics. The molecular classification of MBs is redefining the risk stratification of patients with MB, and has the potential to identify new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of MB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H, Berhoukim R, Amani V, Goumnerova L, Eberhart CG, Lau CC, Olson JM, Gilbertson RJ, Gajjar A, Delattre O, Kool M, Ligon K, Meyerson M, Mesirov JP, Pomeroy SL: Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 29: 1424– 1430, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gajjar A, Chintagumpala M, Ashley D, Kellie S, Kun LE, Merchant TE, Woo S, Wheeler G, Ahern V, Krasin MJ, Fouladi M, Broniscer A, Krance R, Hale GA, Stewart CF, Dauser R, Sanford RA, Fuller C, Lau C, Boyett JM, Wallace D, Gilbertson RJ: Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol 7: 813– 820, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Spiegler BJ, Bouffet E, Greenberg ML, Rutka JT, Mabbott DJ: Change in neurocognitive functioning after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. J Clin Oncol 22: 706– 713, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Gajjar A, Hernan R, Kocak M, Fuller C, Lee Y, McKinnon PJ, Wallace D, Lau C, Chintagumpala M, Ashley DM, Kellie SJ, Kun L, Gilbertson RJ: Clinical, histopathologic, and molecular markers of prognosis: toward a new disease risk stratification system for medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22: 984– 993, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

