Amygdala-Dependent Molecular Mechanisms of the Tac2 Pathway in Fear Learning
- PMID: 27238620
- PMCID: PMC5026739
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2016.77
Amygdala-Dependent Molecular Mechanisms of the Tac2 Pathway in Fear Learning
Abstract
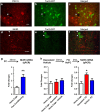
Recently we determined that activation of the tachykinin 2 (Tac2) pathway in the central amygdala (CeA) is necessary and sufficient for the modulation of fear memories. The Tac2 pathway includes the Tac2 gene, which encodes the neuropeptide neurokinin B and its corresponding receptor neurokinin 3 receptor (NK3R). In this study, using Tac2-cre and Tac2-GFP mice, we applied a combination of in vivo (optogenetics) and multiple in vitro techniques to further explore the mechanisms of action within the Tac2 pathway. In transgenic mice that express ChR2 solely in Tac2 neurons, in vivo optogenetic stimulation of CeA Tac2-expressing neurons during fear acquisition enhanced fear memory consolidation and drove action potential firing in vitro. In addition, Tac2-CeA neurons were shown to co-express striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase, which may have an important role in regulating Nk3R signaling during fear conditioning. These data extend our current understanding for the underlying mechanism(s) for the role of the Tac2 pathway in the regulation of fear memory, which may serve as a new therapeutic target in the treatment of fear-related disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Bealer SL, Flynn FW (2003). Central neurokinin 3 receptors increase systemic oxytocin release: interaction with norepinephrine. Exp Neurol 184: 1027–1033. - PubMed
-
- Chao OY, Nikolaus S, Huston JP, de Souza Silva MA (2014). The neurokinin-3 receptor agonist senktide facilitates the integration of memories for object, place and temporal order into episodic memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 114: 178–185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

