Effects of Acute Endurance Exercise on Plasma Protein Profiles of Endurance-Trained and Untrained Individuals over Time
- PMID: 27239103
- PMCID: PMC4867072
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4851935
Effects of Acute Endurance Exercise on Plasma Protein Profiles of Endurance-Trained and Untrained Individuals over Time
Abstract
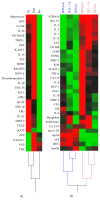
Acute physical exercise and repeated exercise stimuli affect whole-body metabolic and immunologic homeostasis. The aim of this study was to determine plasma protein profiles of trained (EET, n = 19) and untrained (SED, n = 17) individuals at rest and in response to an acute bout of endurance exercise. Participants completed a bicycle exercise test at an intensity corresponding to 80% of their VO2max. Plasma samples were taken before, directly after, and three hours after exercise and analyzed using multiplex immunoassays. Seventy-eight plasma variables were included in the final analysis. Twenty-nine variables displayed significant acute exercise effects in both groups. Seven proteins differed between groups, without being affected by acute exercise. Among these A2Macro and IL-5 were higher in EET individuals while leptin showed elevated levels in SED individuals. Fifteen variables revealed group and time differences with elevated levels for IL-3, IL-7, IL-10, and TNFR2 in EET individuals. An interaction effect could be observed for nine variables including IL-6, MMP-2, MMP-3, and muscle damage markers. The proteins that differ between groups indicate a long-term exercise effect on plasma protein concentrations. These findings might be of importance in the development of exercise-based strategies in the prevention and therapy of chronic metabolic and inflammatory diseases and for training monitoring.
Figures

References
-
- Walsh N. P., Gleeson M., Shephard R. J., et al. Position statement. Part one: immune function and exercise. Exercise Immunology Review. 2011;17:6–63. - PubMed
-
- Huffman K. M., Slentz C. A., Bales C. W., Houmard J. A., Kraus W. E. Relationships between adipose tissue and cytokine responses to a randomized controlled exercise training intervention. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental. 2008;57(4):577–583. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2007.11.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

