Analysis of fibronectin, fibronectin receptor and interleukin-1 in patients with cirrhosis treated by the Yanggan Jieyu decoction
- PMID: 27239143
- PMCID: PMC4842884
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i3.177
Analysis of fibronectin, fibronectin receptor and interleukin-1 in patients with cirrhosis treated by the Yanggan Jieyu decoction
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of the Yanggan Jieyu (YGJY, nourishing the liver and alleviating mental depression) decoction on the plasma concentrations of fibronectin (FN), fibronectin receptor (FNR), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and the activity of interleukin-1 (IL-1) in patients with cirrhosis.
Methods: Thirty-four cases of decompensated cirrhosis were divided into the YGJY decoction treatment group and the control group (patients received standard treatment). FN, FNR and TNF-α were measured by ELISA and expressed as mg/L (FN, FNR) and ng/L (TNF-α). IL-1 was measured by mice thymocyte proliferation using a β scintillation counter and was expressed as cpm.
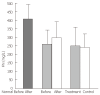
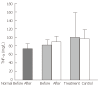
Results: In the YGJY decoction treatment group, FN and TNF-α levels increased significantly (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively), and FNR and IL-1 levels decreased significantly (P < 0.05 and P < 0.05, respectively). In the control group, FN, FNR, TNF-α, and IL-1 levels did not significantly change.
Conclusion: YGJY decoction could prevent hepatic fibrosis by adjusting the plasma levels of FN, FNR, TNF-α and IL-1, which could mediate cirrhosis formation. This data is of clinical significance.
Keywords: Fibronectin; Fibronectin receptors; Interleukin-1; Liver cirrhosis; Traditional Chinese Medicine; Tumor necrosis factor; Yanggan Jieyu decoction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Effects of Tongmai decoction on the perioperative changes of plasma TNF-alpha and IL-6 in patients with femoral fractures].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010 Jul;23(7):500-3. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010. PMID: 20701121 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Experimental study of the influence of Sini decoction on the inflammatory response and the immune function in septic rats].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Mar;26(3):188-92. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.03.013. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24598294 Chinese.
-
Effect of Wenshen-Yanggan Decoction on Movement Disorder and Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons in Mice with Chronic Parkinson's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jun 21;2020:9838295. doi: 10.1155/2020/9838295. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32655672 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression and significance of interleukin-18, 12 and tumor necrosis factor-α in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2011 May;46(5):329-32. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21733366 Chinese.
-
[Recipe-syndrome correlation and pathogenesis mechanism of Yinchenhao Decoction in intervening dimethylnitrosamine induced liver cirrhosis progress in rats].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2010 Aug;30(8):845-50. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21038655 Chinese.
References
-
- Yamauchi M, Nakajima H, Ohata M, Hirakawa J, Mizuhara Y, Nakahara M, Kimura K, Fujisawa K, Kameda H. Detection of fibronectin receptor in sera: its clinical significance as a parameter of hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 1991;14:244–250. - PubMed
-
- Gabrielli GB, Casaril M, Bonazzi L, Baracchino F, Bellisola G, Corrocher R. Plasma fibronectin in liver cirrhosis and its diagnostic value. Clinica Chimica Acta. 1986;160:289–296. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka M, Pham NT, Tsukamoto H. Differential effects of interleukin-1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta 1 on cell proliferation and collagen formation by cultured fat-storing cells. Liver. 1989;9:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Wu H, Wang ZM, Fan JT, Deng JW, Fen TJ. Effect of six kinds of decoctions on experimental autoimmune liver diseases. Bulletin of Hunan Medical University. 1991;16:263–267.
-
- Chen JZ, Li ZM. Internal medicine. Ed 3. Beijing: The People-s Medical Publishing House; 1989. pp. 389–396.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
