Cellular Immune Responses and Immune Escape Mechanisms in Breast Cancer: Determinants of Immunotherapy
- PMID: 27239171
- PMCID: PMC4881254
- DOI: 10.1159/000446061
Cellular Immune Responses and Immune Escape Mechanisms in Breast Cancer: Determinants of Immunotherapy
Abstract
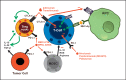
More recently, immunotherapy has emerged as a novel potentially effective therapeutic option also for solid malignancies such as breast cancer (BC). Relevant approaches, however, are determined by the 2 main elements of cancer immunoediting - the elimination of nascent transformed cells by immunosurveillance on the one hand and tumor immune escape on the other hand. Correspondingly, we here review the role of the various cellular immune players within the host-protective system and dissect the mechanisms of immune evasion leading to tumor progression. If the immune balance of disseminated BC cell dormancy (equilibrium phase) is lost, distant metastatic relapse may occur. The relevant cellular antitumor responses and translational immunotherapeutic options will also be discussed in terms of clinical benefit and future directions in BC management.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cellular immunity; Immune escape; Immunoediting; Immunosurveillance; Immunotherapy.
Figures

References
-
- Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565–1570. - PubMed
-
- Ravelli A, Reuben JM, Lanza F, et al. Immune-related strategies driving immunotherapy in breast cancer treatment: a real clinical opportunity. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015;15:689–702. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

