Sarcopenia and mortality among a population-based sample of community-dwelling older adults
- PMID: 27239410
- PMCID: PMC4864252
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12073
Sarcopenia and mortality among a population-based sample of community-dwelling older adults
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenia is a risk-factor for all-cause mortality among older adults, but it is unknown if sarcopenia predisposes older adults to specific causes of death. Further, it is unknown if the prognostic role of sarcopenia differs between males and females, and obese and non-obese individuals.
Methods: A population-based cohort study among 4425 older adults from the Third National Health and Nutrition Survey (1988-1994). Muscle mass was quantified using bioimpedance analysis, and muscle function was quantified using gait speed. Multivariable-adjusted Cox regression analysis examined the relationship between sarcopenia and mortality outcomes.
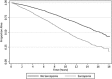
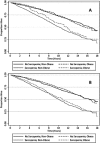
Results: The mean age of study participants was 70.1 years. The prevalence of sarcopenia was 36.5%. Sarcopenia associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality [hazard ratio (HR): 1.29 (95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.13-1.47); P < 0.001] among males and females. Sarcopenia associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular-specific mortality among females [HR: 1.61 (95% CI: 1.22-2.12); P = 0.001], but not among males [HR: 1.07 (95% CI: 0.81-1.40; P = .643); P interaction = 0.079]. Sarcopenia was not associated with cancer-specific mortality among males and females [HR: 1.07 (95% CI: 0.78-1.89); P = 0.672]. Sarcopenia associated with an increased risk of mortality from other causes (i.e. non-cardiovascular and non-cancer) among males and females [HR: 1.32 (95% CI: 1.07-1.62); P = 0.008]. Obesity, defined using body mass index (P interaction = 0.817) or waist circumference (P interaction = 0.219) did not modify the relationship between sarcopenia and all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: Sarcopenia is a prevalent syndrome that is associated with premature mortality among community-dwelling older adults. The prognostic value of sarcopenia may vary by cause-specific mortality and differ between males and females.
Keywords: Body composition; Cohort study; Gait speed; Obesity; Population based; Skeletal muscle.
Figures
References
-
- Goodpaster BH, Park SW, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Nevitt M, Schwartz AV, et al. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2006;61:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Visser M, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, Newman AB, Nevitt M, Rubin SM, et al. Muscle mass, muscle strength, and muscle fat infiltration as predictors of incident mobility limitations in well‐functioning older persons. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2005;60:324–333. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Kupelian V, Visser M, Simonsick EM, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, et al. Strength, but not muscle mass, is associated with mortality in the health, aging and body composition study cohort. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2006;61:72–77. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

