Smoothened Agonist Reduces Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Humanized Mice
- PMID: 27241024
- PMCID: PMC4886511
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26876
Smoothened Agonist Reduces Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Humanized Mice
Abstract
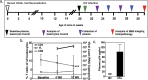
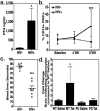
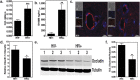
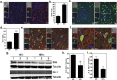
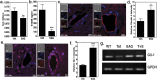
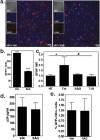
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type-1 (HIV)-associated neurocognitive disorder is characterized by recruitment of activated/infected leukocytes into the CNS via disrupted Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) that contributes to persistent neuro-inflammation. In this report, humanized NOD/scid-IL2Rγc(null) mice were used to establish that impaired Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling is associated with loss of BBB function and neurological damage, and that modulating Shh signaling can rescue these detrimental effects. Plasma viral load, p24 levels and CD4(+) T cells were measured as markers of productive HIV infection. These mice also showed impaired exclusion of Evans blue dye from the brain, increased plasma levels of S100B, an astrocytic protein, and down-regulation of tight junction proteins Occludin and Claudin5, collectively indicating BBB dysfunction. Further, brain tissue from HIV(+) mice indicated reduced synaptic density, neuronal atrophy, microglial activation, and astrocytosis. Importantly, reduced expression of Shh and Gli1 was also observed in these mice, demonstrating diminished Shh signaling. Administration of Shh mimetic, smoothened agonist (SAG) restored BBB integrity and also abated the neuropathology in infected mice. Together, our results suggest a neuroprotective role for Shh signaling in the context of HIV infection, underscoring the therapeutic potential of SAG in controlling HAND pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- McArthur J. C. et al. Dementia in AIDS patients: incidence and risk factors. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Neurology 43, 2245–2252 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

