Factors influencing biochemical recurrence in patients who have received salvage radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 27241314
- PMCID: PMC5507100
- DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.179531
Factors influencing biochemical recurrence in patients who have received salvage radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Several studies have evaluated the risk factors influencing biochemical recurrence (BCR) of prostate cancer in patients receiving salvage radiotherapy (SRT) for BCR after radical prostatectomy (RP), but the results remain conflicting. In this study, we performed a meta-analysis to resolve this conflict. We searched the following databases: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using the following terms in "All fields": "salvage radiation therapy," "salvage IMRT," "S-IMRT," "salvage radiotherapy," "SRT," "radical prostatectomy," "RP," "biochemical recurrence," "BCR," "biochemical relapse." Eleven studies, with a total of 1383 patients, were included in our meta-analysis. Of all the variables, only Gleason score (GS) ≥7 (odds ratio [OR]: 3.82; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.60-5.64) and pathological tumor (pT) stage ≥3a (OR: 1.82; 95% CI: 1.36-2.42) were positively correlated with BCR. However, SRT combined with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) (OR: 0.63; 95% CI: 0.44-0.90) and radiation therapy (RT) dose ≥64 Gy (OR: 0.35; 95% CI: 0.19-0.64) were negatively correlated with BCR. Perineural invasion (OR: 2.64; 95% CI: 1.11-6.26), preoperative prostate-specific antigen (PSA) ≥10 ng ml-1 (OR: 1.36; 95% CI: 0.94-1.96), positive surgical margin (OR: 0.92; 95% CI: 0.7-1.19), and seminal vesicle involvement (SVI) (OR: 1.09; 95% CI: 0.83-1.43) had no effect on BCR. Our meta-analysis indicated that pT stage, GS, RT dose, and SRT combined with ADT may influence BCR, while preoperative PSA, surgical margin, perineural invasion, and SVI have only a weak effect on BCR.
Figures

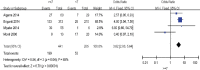






Similar articles
-
Understanding the Impact of Salvage Radiation on the Long-Term Natural History of Biochemically Recurrent Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy.Cancer Med. 2025 Jul;14(13):e70988. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70988. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40567132 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of PSMA PET/CT-guided radiotherapy in biochemical failure patients post-radical prostatectomy: a 5-year follow-up analysis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Aug;52(10):3720-3729. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07255-6. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40186765 Free PMC article.
-
The timing of salvage radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Sep 1;84(1):104-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.069. Epub 2012 Jul 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22795730
-
Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant hormone therapy for localised and locally advanced prostate cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;2006(4):CD006019. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006019.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. PMID: 17054269 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant and Salvage Radiotherapy after Radical Prostatectomy in Prostate Cancer Patients.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):689-709. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.039. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28189428
Cited by
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals intratumoral heterogeneity and potential mechanisms of malignant progression in prostate cancer with perineural invasion.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 9;13:1073232. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1073232. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36712886 Free PMC article.
-
Association between preradiation therapy prostate-specific antigen levels and radiation therapy failure after prostatectomy: a propensity score matched analysis.Prostate Int. 2024 Jun;12(2):90-95. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2024.03.001. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Prostate Int. 2024. PMID: 39036762 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of PSA kinetics on the outcome of hypofractionated salvage radiotherapy for biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after prostatectomy.J Radiat Res. 2020 Nov 16;61(6):908-919. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa074. J Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32888035 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking history, intensity, and duration and risk of prostate cancer recurrence among men with prostate cancer who received definitive treatment.Ann Epidemiol. 2019 Oct;38:4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2019.08.011. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Ann Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 31563295 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing the benefits and harms of radiotherapy post-radical prostatectomy.Transl Androl Urol. 2018 Mar;7(Suppl 1):S128-S131. doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.10.07. Transl Androl Urol. 2018. PMID: 29644180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boorjian SA, Eastham JA, Graefen M, Guillonneau B, Karnes RJ, et al. A critical analysis of the long-term impact of radical prostatectomy on cancer control and function outcomes. Eur Urol. 2012;61:664–75. - PubMed
-
- Mullins JK, Feng Z, Trock BJ, Epstein JI, Walsh PC, et al. The impact of anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy on cancer control: the 30-year anniversary. J Urol. 2012;188:2219–24. - PubMed
-
- Okajima E, Yoshikawa M, Masuda Y, Shimizu K, Tanaka N, et al. Improvement of the surgical curability of locally confined prostate cancer including non-organ-confined high-risk disease through retropubic radical prostatectomy with intentional wide resection. World J Surg Oncol. 2012;10:249. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pfister D, Bolla M, Briganti A, Carroll P, Cozzarini C, et al. Early salvage radiotherapy following radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2014;65:1034–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

