Treatment of Rats with Apocynin Has Considerable Inhibitory Effects on Arylamine N-Acetyltransferase Activity in the Liver
- PMID: 27242013
- PMCID: PMC4886258
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26906
Treatment of Rats with Apocynin Has Considerable Inhibitory Effects on Arylamine N-Acetyltransferase Activity in the Liver
Abstract
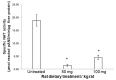
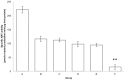
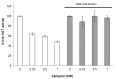
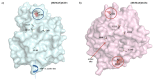
The effect of apocynin on the activity of arylamine N-acetyltransferases (NATs) in excised liver samples was examined using eighteen Sprague-Dawley rats. Three groups of six animals each were fed a normal diet alone or a treatment of 50 or 100 mg/kg/day of apocynin via gavages for eight (8) weeks. Chronic in vivo administration of apocynin led to significant (p < 0.001) reduction of in vitro liver NAT activity up to 93% as compared with untreated rats (18.80 ± 2.10 μmols p-anisidine/min/μg liver protein). In vitro exposure of untreated liver homogenates to apocynin led to a dose-dependent inhibition of NAT activity with IC50 = 0.69 ± 0.02 mM. In silico modelling of apocynin tautomers and radical species into human NAT crystal structures supported the hypothesis that thiol functionalities in NAT enzymes may be crucial in apocynin binding. The involvement of human NAT enzymes in different pathological conditions, such as cancer, has encouraged the research for selective NAT inhibitors in both humans and animal models with possible chemopreventive properties.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arylamine N-acetyltransferases: a structural perspective.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jun;169(4):748-60. doi: 10.1111/bph.12182. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23517104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and mechanism of arylamine N-acetyltransferases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(15):1641-54. doi: 10.2174/156802606778108979. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16918475 Review.
-
Effects of luteolin on arylamine N-acetyltransferase activity in rat blood and liver.Phytomedicine. 2000 Mar;7(1):49-54. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80021-5. Phytomedicine. 2000. PMID: 10782490
-
Differences between murine arylamine N-acetyltransferase type 1 and human arylamine N-acetyltransferase type 2 defined by substrate specificity and inhibitor binding.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Nov 29;15:68. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-15-68. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25432241 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity alkylation of hamster hepatic arylamine N-acetyltransferases: isolation of a modified cysteine residue.Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;42(1):82-93. Mol Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1635555
Cited by
-
Evaluating the potential of Kalanchoe pinnata, Piper amalago amalago, and other botanicals as economical insecticidal synergists against Anopheles gambiae.Malar J. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12936-025-05254-4. Malar J. 2025. PMID: 39844288 Free PMC article.
-
Edaravone and Acetovanillone Upregulate Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling and Prevent Cyclophosphamide Cardiotoxicity in Rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Nov 30;14:5275-5288. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S281854. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33299300 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of N-Acetyltransferase 2-Mediated Drug Interactions of Amifampridine: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence of Drug Interactions with Acetaminophen.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 11;15(5):1471. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051471. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242713 Free PMC article.
-
Glaucarubulone glucoside from Castela macrophylla suppresses MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth and attenuates benzo[a]pyrene-mediated CYP1A gene induction.J Appl Toxicol. 2017 Jul;37(7):873-883. doi: 10.1002/jat.3436. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Appl Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28138972 Free PMC article.
-
A Microbiological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Study of the Effects of Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid, on Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the Enzymes Implicated in Its Cell Wall: A Link Between Mycobacterial Infection and Autoimmune Diseases.Mar Drugs. 2019 Nov 14;17(11):641. doi: 10.3390/md17110641. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31739453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons J. M., Hart B. A., Ching T. R. I. V., Van Dijk H. & Labadie R.P. Metabolic activation of natural phenols into selective oxidative burst agonists by activated human neutrophils. Free Radical Biol. Med. 8, 251–258 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Ximenes V. F., Kanegae M. P. P., Rissato S. R. & Galhiane M. S. The oxidation of apocynin catalyzed by myeloperoxidase: Proposal for NADPH oxidase inhibition. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 457, 134–141 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

