Impact of Exercise and Education in Adults of Lubbock, Texas: Implications for Better Lifestyle
- PMID: 27242507
- PMCID: PMC4861719
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00085
Impact of Exercise and Education in Adults of Lubbock, Texas: Implications for Better Lifestyle
Abstract
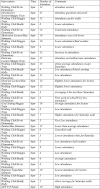
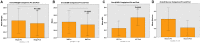
The objective of our study was to evaluate the exercise and educational intervention in the city of Lubbock via GET FiT Lubbock (GFL) program. The GFL program was designed to increase exercise and educational opportunities, which positively impact health risk factors in Lubbock residents. The GFL program design included the recruitment of subjects to participate on a team that consisted of four individuals, each subject tracked their exercise minutes, and their educational session attendance. The tracking of exercise and educational sessions was done on the GFL website. Biometric testing was conducted pre- and post- intervention. The program was located within the Lubbock community in places that were close to their place of residence. The intervention included walking and educational sessions, including goal setting lectures, nutrition information, and exercise demonstrations. Study participants, included male and female adults who tracked their exercise time and educational sessions. Exercise minutes and educational session attendance were self-reported. Our data analysis revealed that significant difference was found between pre- and post- intervention measures, including weight, body mass index (BMI), high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Significant difference was found for weight, BMI, and HDL in females. Based on these findings, we conclude that the intervention showed positive effects on exercise and lifestyle.
Keywords: aging; behavioral research; community based participatory research; intervention studies; nutrition and exercise education.
Figures
References
-
- Carr B. (2011). Board of Health Report. Available online at: http://www.publichealthlubbock.com/reports/If%20you%20live%20in%20Lubboc...
-
- Carr B. (2014). State of the Health of Lubbock Report. Available online at: http://www.publichealthlubbock.com/reports/stateofhealthinlubbock2013.pdf January, 2014
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

