A Review of Sleep and Its Disorders in Patients with Parkinson's Disease in Relation to Various Brain Structures
- PMID: 27242523
- PMCID: PMC4876118
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00114
A Review of Sleep and Its Disorders in Patients with Parkinson's Disease in Relation to Various Brain Structures
Abstract
Sleep is an indispensable normal physiology of the human body fundamental for healthy functioning. It has been observed that Parkinson's disease (PD) not only exhibits motor symptoms, but also non-motor symptoms such as metabolic irregularities, altered olfaction, cardiovascular dysfunction, gastrointestinal complications and especially sleep disorders which is the focus of this review. A good understanding and knowledge of the different brain structures involved and how they function in the development of sleep disorders should be well comprehended in order to treat and alleviate these symptoms and enhance quality of life for PD patients. Therefore it is vital that the normal functioning of the body in relation to sleep is well understood before proceeding on to the pathophysiology of PD correlating to its symptoms. Suitable treatment can then be administered toward enhancing the quality of life of these patients, perhaps even discovering the cause for this disease.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease (PD); REMS behavior disorder (RBD); dopamine; hypocretin; non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREMS); rapid eye movement sleep (REMS); sleep; suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN).
Figures
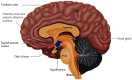
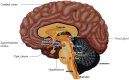
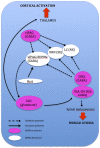
References
-
- Albanese A., Altavista M., Rossi P. (1985). Organization of central nervous system dopaminergic pathways. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 22, 3–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

