Rifaximin Improves Clostridium difficile Toxin A-Induced Toxicity in Caco-2 Cells by the PXR-Dependent TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 27242527
- PMCID: PMC4860461
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00120
Rifaximin Improves Clostridium difficile Toxin A-Induced Toxicity in Caco-2 Cells by the PXR-Dependent TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
Background: Clostridium difficile infections (CDIs) caused by Clostridium difficile toxin A (TcdA) lead to severe ulceration, inflammation and bleeding of the colon, and are difficult to treat.
Aim: The study aimed to evaluate the effect of rifaximin on TcdA-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells and investigate the role of PXR in its mechanism of action.
Methods: Caco-2 cells were incubated with TcdA and treated with rifaximin (0.1-10 μM) with or without ketoconazole (10 μM). The transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and viability of the treated cells was determined. Also, the expression of zona occludens-1 (ZO-1), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) was determined.
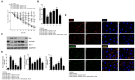
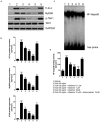
Results: Rifaximin treatment (0.1, 1.0, and 10 μM) caused a significant and concentration-dependent increase in the TEER of Caco-2 cells (360, 480, and 680% vs. TcdA treatment) 24 h after the treatment and improved their viability (61, 79, and 105%). Treatment also concentration-dependently decreased the expression of Bax protein (-29, -65, and -77%) and increased the expression of ZO-1 (25, 54, and 87%) and occludin (71, 114, and 262%) versus TcdA treatment. The expression of TLR4 (-33, -50, and -75%), MyD88 (-29, -60, and -81%) and TAK1 (-37, -63, and -79%) were also reduced with rifaximin versus TcdA treatment. Ketoconazole treatment inhibited these effects.
Conclusion: Rifaximin improved TcdA-induced toxicity in Caco-2 cells by the PXR-dependent TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway mechanism, and may be useful in the treatment of CDIs.
Keywords: Caco-2 cells; Clostridium difficile toxin A; pregnane X receptor; pseudomembranous colitis; rifaximin.
Figures
References
-
- Cash B. D., Lacy B. E., Rao T., Earnest D. L. (2016). Rifaximin and eluxadoline – newly approved treatments for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: what is their role in clinical practice alongside alosetron? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 17 311–322. 10.1517/14656566.2016.1118052 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

