Shelf-Life of Chlorine Solutions Recommended in Ebola Virus Disease Response
- PMID: 27244552
- PMCID: PMC4887112
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156136
Shelf-Life of Chlorine Solutions Recommended in Ebola Virus Disease Response
Abstract
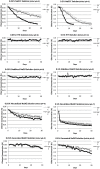
In Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreaks, it is widely recommended to wash living things (handwashing) with 0.05% (500 mg/L) chlorine solution and non-living things (surfaces, personal protective equipment, dead bodies) with 0.5% (5,000 mg/L) chlorine solution. Chlorine solutions used in EVD response are primarily made from powdered calcium hypochlorite (HTH), granular sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC), and liquid sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), and have a pH range of 5-11. Chlorine solutions degrade following a reaction highly dependent on, and unusually sensitive to, pH, temperature, and concentration. We determined the shelf-life of 0.05% and 0.5% chlorine solutions used in EVD response, including HTH, NaDCC, stabilized NaOCl, generated NaOCl, and neutralized NaOCl solutions. Solutions were stored for 30 days at 25, 30, and 35°C, and tested daily for chlorine concentration and pH. Maximum shelf-life was defined as days until initial concentration fell to <90% of initial concentration in ideal laboratory conditions. At 25-35°C, neutralized-NaOCl solutions (pH = 7) had a maximum shelf-life of a few hours, NaDCC solutions (pH = 6) 2 days, generated NaOCl solutions (pH = 9) 6 days, and HTH and stabilized NaOCl solutions (pH 9-11) >30 days. Models were developed for solutions with maximum shelf-lives between 1-30 days. Extrapolating to 40°C, the maximum predicted shelf-life for 0.05% and 0.5% NaDCC solutions were 0.38 and 0.82 hours, respectively; predicted shelf-life for 0.05% and 0.5% generated NaOCl solutions were >30 and 5.4 days, respectively. Each chlorine solution type offers advantages and disadvantages to responders, as: NaDCC is an easy-to-import high-concentration effervescent powder; HTH is similar, but forms a precipitate that may clog pipes; and, NaOCl solutions can be made locally, but are difficult to transport. We recommend responders chose the most appropriate source chlorine compound for their use, and ensure solutions are stored at appropriate temperatures and used or replaced before expiring.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy, Precision, Ease-Of-Use, and Cost of Methods to Test Ebola-Relevant Chlorine Solutions.PLoS One. 2016 May 31;11(5):e0152442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152442. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27243817 Free PMC article.
-
Seeking Clearer Recommendations for Hand Hygiene in Communities Facing Ebola: A Randomized Trial Investigating the Impact of Six Handwashing Methods on Skin Irritation and Dermatitis.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 28;11(12):e0167378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167378. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28030544 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The antibacterial properties of sodium hypochlorite and sodium dichloroisocyanurate as hospital disinfectants.J Hosp Infect. 1985 Mar;6(1):20-30. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6701(85)80014-1. J Hosp Infect. 1985. PMID: 2859319
-
Influence of pH changes on chlorine-containing endodontic irrigating solutions.Int Endod J. 2011 Sep;44(9):792-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01911.x. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Int Endod J. 2011. PMID: 21658076 Review.
-
Sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) tablets as an alternative to sodium hypochlorite for the routine treatment of drinking water at the household level.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2006 Mar;209(2):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2005.11.004. Epub 2006 Jan 4. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2006. PMID: 16387550 Review.
Cited by
-
Back to Basics: Choosing the Appropriate Surface Disinfectant.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 21;10(6):613. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060613. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Disinfection Characteristics of Ebola Virus Outbreak Variants.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 2;6:38293. doi: 10.1038/srep38293. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27910909 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of Free Available Chlorine Levels in Dilute Sodium Hypochlorite Solutions over a 6-Week Period.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022 Mar 1;61(2):181-187. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-21-000080. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35109965 Free PMC article.
-
Excessive use of disinfectants against COVID-19 posing a potential threat to living beings.Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:159-168. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2021.02.008. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33688633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Face mask and medical waste disposal during the novel COVID-19 pandemic in Asia.Case Stud Chem Environ Eng. 2020 Sep;2:100052. doi: 10.1016/j.cscee.2020.100052. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng. 2020. PMID: 38620353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO | Ebola virus disease. World Health Organization. n.d. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs103/en/. Accessed 9 November 2015.
-
- Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease) Signs and Symptoms. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. n.d. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/symptoms/index.html. Accessed 14 October 2015.
-
- Ebola Situation Report. World Health Organization; 2016. Available: http://apps.who.int/ebola/current-situation/ebola-situation-report-20-ja...
-
- Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease) Transmission. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. n.d. http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/transmission/index.html. Accessed 14 October 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical