Preserved Nephrogenesis Following Partial Nephrectomy in Early Neonates
- PMID: 27244673
- PMCID: PMC4886582
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26792
Preserved Nephrogenesis Following Partial Nephrectomy in Early Neonates
Abstract
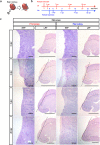
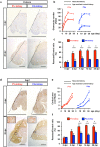
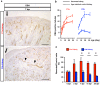
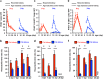
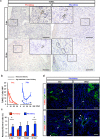
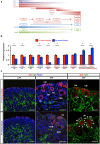
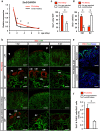
Reconstitution of total nephron segments after resection in the adult kidney has not been achieved; however, whether the neonatal kidney can maintain the capacity for neo-nephrogenesis after resection is unknown. We performed partial resection of the kidney in neonatal rats on postnatal days 1 (P1x kidney) and 4 (P4x kidney) and examined morphological changes and relevant factors. The P1x kidney bulged into the newly formed cortex from the wound edge, while nephrogenesis failure was prominent in the P4x kidney. Twenty-eight days post-resection, the glomerular number, cortex area, and collecting duct were preserved in the P1x kidney, whereas these parameters were markedly decreased in the P4x kidney. During normal development, Six2 expression and Six2+ nephron progenitor cells in the cap mesenchyme both rapidly disappear after birth. However, time course analysis for the P1x kidney showed that Six2 expression and Six2+ cells were well preserved in the tissue surrounding the resected area even 2 days after resection. In conclusion, our results indicate that kidneys in early neonate rats retain the capability for neo-nephrogenesis after resection; however, this ability is lost soon after birth, which may be attributed to a declining amount of Six2+ cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neonatal nephron loss during active nephrogenesis results in altered expression of renal developmental genes and markers of kidney injury.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Dec 1;53(12):509-517. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00059.2021. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34704838
-
Postembryonic Nephrogenesis and Persistence of Six2-Expressing Nephron Progenitor Cells in the Reptilian Kidney.PLoS One. 2016 May 4;11(5):e0153422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153422. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27144443 Free PMC article.
-
Repair after nephron ablation reveals limitations of neonatal neonephrogenesis.JCI Insight. 2017 Jan 26;2(2):e88848. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.88848. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28138555 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic States of nephron progenitors and epithelial differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Jun;116(6):893-902. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25048. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25560433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regenerating the nephron with human pluripotent stem cells.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2015 Apr;20(2):187-92. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000177. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25695593 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Autologous Cell Therapy to Stabilize Function in Diabetes-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: Corroboration of Mechanistic Action With Cell Marker Analysis.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Apr 21;7(7):1619-1629. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.04.014. eCollection 2022 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 35812284 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Differences following Partial Salivary Gland Resection.J Dent Res. 2020 Jan;99(1):79-88. doi: 10.1177/0022034519889026. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 31765574 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

