Childhood Sexual Violence Against Boys: A Study in 3 Countries
- PMID: 27244799
- PMCID: PMC5819871
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2015-3386
Childhood Sexual Violence Against Boys: A Study in 3 Countries
Abstract
Background and objective: Globally, little evidence exists on sexual violence against boys. We sought to produce the first internationally comparable estimates of the magnitude, characteristics, risk factors, and consequences of sexual violence against boys in 3 diverse countries.
Methods: We conducted nationally representative, multistage cluster Violence Against Children Surveys in Haiti, Kenya, and Cambodia among males aged 13 to 24 years. Differences between countries for boys experiencing sexual violence (including sexual touching, attempted sex, and forced/coerced sex) before age 18 years were examined by using χ(2) and logistic regression analyses.
Results: In Haiti, Kenya, and Cambodia, respectively, 1459, 1456, and 1255 males completed surveys. The prevalence of experiencing any form of sexual violence ranged from 23.1% (95% confidence Interval [CI]: 20.0-26.2) in Haiti to 14.8% (95% CI: 12.0-17.7) in Kenya, and 5.6% (95% CI: 4.0-7.2) in Cambodia. The largest share of perpetrators in Haiti, Kenya, and Cambodia, respectively, were friends/neighbors (64.7%), romantic partners (37.2%), and relatives (37.0%). Most episodes occurred inside perpetrators' or victims' homes in Haiti (60.4%), contrasted with outside the home in Kenya (65.3%) and Cambodia (52.1%). The most common time period for violence in Haiti, Kenya, and Cambodia was the afternoon (55.0%), evening (41.3%), and morning (38.2%), respectively. Adverse health effects associated with violence were common, including increased odds of transactional sex, alcohol abuse, sexually transmitted infections, anxiety/depression, suicidal ideation/attempts, and violent gender attitudes.
Conclusions: Differences were noted between countries in the prevalence, characteristics, and risk factors of sexual violence, yet associations with adverse health effects were pervasive. Prevention strategies tailored to individual locales are needed.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
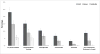
References
-
- Reza A, Breiding MJ, Gulaid J, et al. Sexual violence and its health consequences for female children in Swaziland: a cluster survey study. Lancet. 2009;373(9679):1966–1972. - PubMed
-
- Jewkes RK, Dunkle K, Nduna M, Shai N. Intimate partner violence, relationship power inequity, and incidence of HIV infection in young women in South Africa: a cohort study. Lancet. 2010;376(9734):41–48. - PubMed
-
- United Nations. UNiTE. [Accessed May 15, 2014];Secretary-General’s Campaign to End Violence Against Women. Available at: http://endviolence.un.org/index.shtml.
-
- Conant E. [Accessed May 15 2013];Nigeria’s Schoolgirl Kidnappings Cast Light on Child Trafficking. Available at: http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/05/140515-nigeria-girls-bok....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

