EGR1 mediates miR-203a suppress the hepatocellular carcinoma cells progression by targeting HOXD3 through EGFR signaling pathway
- PMID: 27244890
- PMCID: PMC5216724
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9605
EGR1 mediates miR-203a suppress the hepatocellular carcinoma cells progression by targeting HOXD3 through EGFR signaling pathway
Abstract
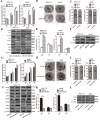
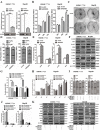
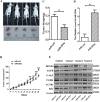
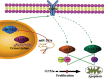
EGR1 plays a critical role in cancer progression. However, its precise role in hepatocellular carcinoma has not been elucidated. In this study, we found that the overexpression of EGR1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and increases cell apoptosis by binding to the miR-203a promoter sequence. In addition, we investigated the function of miR-203a on progression of HCC cells. We verified that the effect of overexpression of miR-203a is consistent with that of EGR1 in regulation of cell progression. Through bioinformatic analysis and luciferase assays, we confirmed that miR-203a targets HOXD3. Silencing HOXD3 could block transition of the G2/M phase, increase cell apoptosis, decrease the expression of cell cycle and apoptosis-related proteins, EGFR, p-AKT, p-ERK, CCNB1, CDK1 and Bcl2 by targeting EGFR through EGFR/AKT and ERK cell signaling pathways. Likewise, restoration of HOXD3 counteracted the effects of miR-203a expression.In conclusion, our findings are the first to demonstrate that EGR1 is a key player in the transcriptional control of miR-203a, and that miR-203a acts as an anti-oncogene to suppress HCC tumorigenesis by targeting HOXD3 through EGFR-related cell signaling pathways.
Keywords: EGR1; HOXD3; cell progression; hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-203a.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HOXD3 targeted by miR-203a suppresses cell metastasis and angiogenesis through VEGFR in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 5;8(1):2431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20859-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29402992 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-203a functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer by targeting SIX4.Neoplasma. 2019 Mar 5;66(2):211-221. doi: 10.4149/neo_2018_180512N312. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Neoplasma. 2019. PMID: 30509104
-
miR-203a controls keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation via targeting the stemness-associated factor ΔNp63 and establishing a regulatory circuit with SNAI2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):241-249. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.131. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28754589
-
Is EGR1 a potential target for prostate cancer therapy?Future Oncol. 2009 Sep;5(7):993-1003. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.67. Future Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19792968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Transcription Factor EGR1 in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 24;11:642547. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.642547. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD24 isoform a promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion and is downregulated by EGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Feb 28;12:1705-1716. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S196506. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30881025 Free PMC article.
-
miR-3928v is induced by HBx via NF-κB/EGR1 and contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy by down-regulating VDAC3.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 29;37(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0681-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 28;41(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02580-2. PMID: 29378599 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The circular RNA PVT1/miR-203/HOXD3 pathway promotes the progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma.Biol Open. 2019 Sep 24;8(9):bio043687. doi: 10.1242/bio.043687. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31551242 Free PMC article.
-
MBD1/HDAC3-miR-5701-FGFR2 axis promotes the development of gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jul 22;14(14):5878-5894. doi: 10.18632/aging.204190. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35876658 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of miR-191-5p level and its potential signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma: a study validated by microarray and in-house qRT-PCR with 1,291 clinical samples.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Apr 1;12(4):1439-1456. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Zhang JB, Qin Y, Wang W, Wei L, Teng Y, Guo L, Zhang B, Lin Z, Liu J, Ren ZG, Ye QH, Xie Y. PROX1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by way of up-regulating hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and protein stability. Hepatology. 2013;58:692–705. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Hong JM, Yoon KA, Kim N, Cho DW, Choi JY, Lee IK, Kim SY. Early growth response 2 negatively modulates osteoclast differentiation through upregulation of Id helix-loop-helix proteins. Bone. 2012;51:643–650. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

