Rapid and sensitive detection of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with fluorescence probe targeting dipeptidylpeptidase IV
- PMID: 27245876
- PMCID: PMC4887889
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26399
Rapid and sensitive detection of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with fluorescence probe targeting dipeptidylpeptidase IV
Abstract
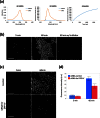
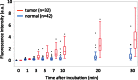
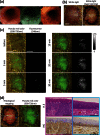
Early detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is an important prognosticator, but is difficult to achieve by conventional endoscopy. Conventional lugol chromoendoscopy and equipment-based image-enhanced endoscopy, such as narrow-band imaging (NBI), have various practical limitations. Since fluorescence-based visualization is considered a promising approach, we aimed to develop an activatable fluorescence probe to visualize ESCCs. First, based on the fact that various aminopeptidase activities are elevated in cancer, we screened freshly resected specimens from patients with a series of aminopeptidase-activatable fluorescence probes. The results indicated that dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP-IV) is specifically activated in ESCCs, and would be a suitable molecular target for detection of esophageal cancer. Therefore, we designed, synthesized and characterized a series of DPP-IV-activatable fluorescence probes. When the selected probe was topically sprayed onto endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) or surgical specimens, tumors were visualized within 5 min, and when the probe was sprayed on biopsy samples, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy reached 96.9%, 85.7% and 90.5%. We believe that DPP-IV-targeted activatable fluorescence probes are practically translatable as convenient tools for clinical application to enable rapid and accurate diagnosis of early esophageal cancer during endoscopic or surgical procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Enzinger P. C. & Mayer R. J. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 349, 2241–2252 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Katada C. et al.. Clinical outcome after endoscopic mucosal resection for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invading the muscularis mucosae–a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Endoscopy. 39, 779–783 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Katada C., Muto M., Manabe T., Ohtsu A. & Yoshida S. Local recurrence of squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus after EMR. Gastrointest Endosc. 61, 219–225 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Shimizu Y. et al.. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for treatment of early stage hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 64, 255–259 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ono S. et al.. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 70, 860–866 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

