The ROS Wheel: Refining ROS Transcriptional Footprints
- PMID: 27246095
- PMCID: PMC4936575
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.16.00420
The ROS Wheel: Refining ROS Transcriptional Footprints
Abstract
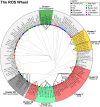
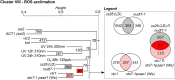
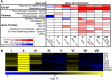
In the last decade, microarray studies have delivered extensive inventories of transcriptome-wide changes in messenger RNA levels provoked by various types of oxidative stress in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Previous cross-study comparisons indicated how different types of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their subcellular accumulation sites are able to reshape the transcriptome in specific manners. However, these analyses often employed simplistic statistical frameworks that are not compatible with large-scale analyses. Here, we reanalyzed a total of 79 Affymetrix ATH1 microarray studies of redox homeostasis perturbation experiments. To create hierarchy in such a high number of transcriptomic data sets, all transcriptional profiles were clustered on the overlap extent of their differentially expressed transcripts. Subsequently, meta-analysis determined a single magnitude of differential expression across studies and identified common transcriptional footprints per cluster. The resulting transcriptional footprints revealed the regulation of various metabolic pathways and gene families. The RESPIRATORY BURST OXIDASE HOMOLOG F-mediated respiratory burst had a major impact and was a converging point among several studies. Conversely, the timing of the oxidative stress response was a determining factor in shaping different transcriptome footprints. Our study emphasizes the need to interpret transcriptomic data sets in a systematic context, where initial, specific stress triggers can converge to common, aspecific transcriptional changes. We believe that these refined transcriptional footprints provide a valuable resource for assessing the involvement of ROS in biological processes in plants.
© 2016 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Chaouch S, Queval G, Noctor G (2012) AtRbohF is a crucial modulator of defence-associated metabolism and a key actor in the interplay between intracellular oxidative stress and pathogenesis responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69: 613–627 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

