Impact of Disease Management Programs on HbA1c Values in Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Germany
- PMID: 27246670
- PMCID: PMC5375061
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296816651633
Impact of Disease Management Programs on HbA1c Values in Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Germany
Abstract
Background: The aim was to analyze the impact of disease management programs on HbA1c values in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in Germany.
Methods: This study included 9017 patients followed in disease management programs (DMPs) who started an antihyperglycemic treatment upon inclusion in a DMP. Standard care (SC) patients were included after individual matching (1:1) to DMP cases based on age, gender, physician (diabetologist versus nondiabetologist care), HbA1c values at baseline, and index year. The main outcome was the share of patients with HbA1c <7.5% or 6.5% after at least 6 months and less than 12 months of therapy in DMP and SC groups. Multivariate logistic regression models were fitted with HbA1c level as a dependent variable and the potential predictor (DMP versus SC).
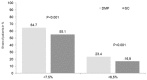
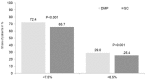
Results: The mean age was 64.3 years and 54.7% of the patients were men. The mean HbA1c level at baseline was equal to 8.7%. In diabetologist practices, 64.7% of DMP patients and 55.1% of SC patients had HbA1c levels <7.5%, while 23.4% of DMP patients and 16.9% of SC patients had HbA1c levels <6.5% ( P values < .001). By comparison, in general practices, 72.4% of DMP patients and 65.7% of SC patients had HbA1c levels <7.5%, while 29.0% of DMP patients and 25.4% of SC patients had HbA1c levels <6.5% ( P values < .001). DMPs increased the likelihood of HbA1c levels lower than 7.5% or 6.5% after 6 months of therapy in both diabetologist and general care practices.
Conclusion: The present study indicates that the enrollment of T2DM patients in DMPs has a positive impact on HbA1c values in Germany.
Keywords: DMP; HbA1c; disease management program; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of the Disease Management Program on HbA1c Value in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Retrospective Comparison between Disease Management Programs and Standard Care].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2017 Oct;142(21):e148-e155. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-104267. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2017. PMID: 28915520 German.
-
Risk of Nonfatal Stroke in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Retrospective Comparison Between Disease Management Programs and Standard Care.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017 Jul;11(4):808-813. doi: 10.1177/1932296817691304. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28300432 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription Patterns and the Cost of Antihyperglycemic Drugs in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Germany.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017 Jan;11(1):123-127. doi: 10.1177/1932296816658746. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 27402240 Free PMC article.
-
An alternative approach to modelling HbA1c trajectories in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 May;19(5):628-634. doi: 10.1111/dom.12865. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28026908
-
Regular Exploratory Examination of the Need for Revision of DMPs -- A Feasibility Study Using the Example of the DMP "CHD" [Internet].Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2014 Oct 7. Executive Summary of Working Paper No. GA14-06. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2014 Oct 7. Executive Summary of Working Paper No. GA14-06. PMID: 27905797 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
[Photo-based examination for diabetic eye pathologies in a German ophthalmological practice without personal doctor-patient contact].Ophthalmologie. 2023 Mar;120(3):301-308. doi: 10.1007/s00347-022-01737-w. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Ophthalmologie. 2023. PMID: 36169715 German.
-
Metabolic Control, Diabetic Complications and Drug Therapy in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Secondary and Tertiary Care between 2004 and 2019.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 1;20(3):2631. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032631. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36768000 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonality of Insulin Use in German Outpatients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017 Sep;11(5):996-1000. doi: 10.1177/1932296817703994. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28420259 Free PMC article.
-
Association between full monitoring of biomedical and lifestyle target indicators and HbA1c level in primary type 2 diabetes care: an observational cohort study (ELZHA-cohort 1).BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 13;9(3):e027208. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027208. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30867205 Free PMC article.
-
[Osteoporosis-risk evaluation and case finding].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023 Oct;52(10):787-792. doi: 10.1007/s00132-023-04431-0. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37610530 Review. German.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. 2015. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/. Accessed April 1, 2016.
-
- Statistics—Deutsches Zentrum für Diabetesforschung (DZD). 2015. Available at: https://www.dzd-ev.de/en/diabetes-the-disease/statistics/index.html. Accessed April 1, 2016.
-
- Köster I, Huppertz E, Hauner H, Schubert I. Costs of diabetes mellitus (CoDiM) in Germany, direct per-capita costs of managing hyperglycaemia and diabetes complications in 2010 compared to 2001. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2014;122:510-516. - PubMed
-
- Ellrodt G, Cook DJ, Lee J, Cho M, Hunt D, Weingarten S. Evidence-based disease management. JAMA. 1997;278:1687-1692. - PubMed
-
- Busse R. Disease management programs in Germany’s statutory health insurance system. Health Aff Proj Hope. 2004;23:56-67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

