Hyperuricemia and the Prognosis of Hypertensive Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27247021
- PMCID: PMC8031654
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12855
Hyperuricemia and the Prognosis of Hypertensive Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
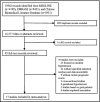
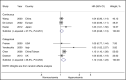
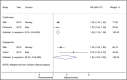
The aim of this study was to assess the prognostic value of hyperuricemia in patients with established hypertension by systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. MEDLINE, Embase, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database were searched through January 2015. Seventeen cohort studies were included and their methodological quality was moderate to high, with Newcastle-Ottawa Scale scores ranging from 6 to 9. Random-effects model meta-analyses showed that in terms of adjusted categorical data, hyperuricemia significantly correlated with cardiovascular diseases in hypertensive patients (hazard ratio [HR], 1.51; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13-2.03), all-cause mortality (HR, 1.12; 95%CI, 1.02-1.23), and diabetes (HR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.02-3.30) but not with stroke (HR, 0.85; 95%CI, 0.57-1.27); while, in terms of adjusted continuous data, the corresponding pooled HRs were 1.17 (95% CI, 1.07-1.27), 1.05 (95% CI, 0.98-1.13), 1.28 (95% CI, 1.18-1.38), and 1.06 (95% CI, 0.98-1.16), respectively. The findings of our meta-analysis suggest that hyperuricemia could slightly increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in patients with hypertension.
©2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Wu XW, Muzny DM, Lee CC, et al. Two independent mutational events in the loss of urate oxidase during hominoid evolution. J Mol Evol. 1992;34:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Brand FN, McGee DL, Kannel WB, et al. Hyperuricemia as a risk factor of coronary heart disease: the Framingham Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;121:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Freedman DS, Williamson DF, Gunter EW, et al. Relation of serum uric acid to mortality and ischemic heart disease. The NHANES I Epidemiologic Follow‐up Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:637–644. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- Viazzi F, Parodi D, Leoncini G, et al. Serum uric acid and target organ damage in primary hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;45:991–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

