Polyamine transporter in Streptococcus pneumoniae is essential for evading early innate immune responses in pneumococcal pneumonia
- PMID: 27247105
- PMCID: PMC4887915
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26964
Polyamine transporter in Streptococcus pneumoniae is essential for evading early innate immune responses in pneumococcal pneumonia
Abstract
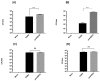
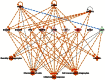
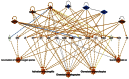
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial etiology of pneumococcal pneumonia in adults worldwide. Genomic plasticity, antibiotic resistance and extreme capsular antigenic variation complicates the design of effective therapeutic strategies. Polyamines are ubiquitous small cationic molecules necessary for full expression of pneumococcal virulence. Polyamine transport system is an attractive therapeutic target as it is highly conserved across pneumococcal serotypes. In this study, we compared an isogenic deletion strain of S. pneumoniae TIGR4 in polyamine transport operon (ΔpotABCD) with the wild type in a mouse model of pneumococcal pneumonia. Our results show that the wild type persists in mouse lung 24 h post infection while the mutant strain is cleared by host defense mechanisms. We show that intact potABCD is required for survival in the host by providing resistance to neutrophil killing. Comparative proteomics analysis of murine lungs infected with wild type and ΔpotABCD pneumococci identified expression of proteins that could confer protection to wild type strain and help establish infection. We identified ERM complex, PGLYRP1, PTPRC/CD45 and POSTN as new players in the pathogenesis of pneumococcal pneumonia. Additionally, we found that deficiency of polyamine transport leads to up regulation of the polyamine synthesis genes speE and cad in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyamine transporter potABCD is required for virulence of encapsulated but not nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 6;12(6):e0179159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179159. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28586394 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine biosynthesis and transport mechanisms are crucial for fitness and pathogenesis of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Feb;157(Pt 2):504-515. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.042564-0. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 20966092
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae Evades Host Cell Phagocytosis and Limits Host Mortality Through Its Cell Wall Anchoring Protein PfbA.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Aug 20;9:301. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00301. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31482074 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Role of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Oxidant in Pneumococcal Pneumonia.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Apr 20;34(12):962-978. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7964. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 32283950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene elements that regulate Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence and immunity evasion.Curr Gene Ther. 2013 Feb;13(1):51-64. doi: 10.2174/156652313804806615. Curr Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23189947 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Changes in the Gut Microbiome Contribute to Transforming Growth Factor β-Deficient Colon Cancer.mSystems. 2017 Sep 26;2(5):e00065-17. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00065-17. eCollection 2017 Sep-Oct. mSystems. 2017. PMID: 28951889 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine transporter potABCD is required for virulence of encapsulated but not nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 6;12(6):e0179159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179159. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28586394 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic induced synthesis of microbiota polyamine as a nutraceutical for metabolic syndrome and obesity-related type 2 diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 13;13:1094258. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1094258. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changed Expression of Cytoskeleton Proteins During Lung Injury in a Mouse Model of Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 8;9:928. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00928. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29867838 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine Decarboxylase Is Essential for Pneumococcal Stress Responses.Pathogens. 2021 Mar 2;10(3):286. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10030286. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33801541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garenne M., Ronsmans C. & Campbell H. The magnitude of mortality from acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years in developing countries. World health statistics quarterly 45, 180–191 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Bridy-Pappas A. E., Margolis M. B., Center K. J. & Isaacman D. J. Streptococcus pneumoniae: description of the pathogen, disease epidemiology, treatment, and prevention. Pharmacotherapy 25, 1193–1212 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. (Public Health Foundation, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

