Small molecule dual-inhibitors of TRPV4 and TRPA1 for attenuation of inflammation and pain
- PMID: 27247148
- PMCID: PMC4887995
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26894
Small molecule dual-inhibitors of TRPV4 and TRPA1 for attenuation of inflammation and pain
Abstract
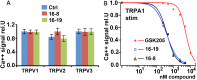
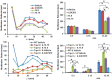
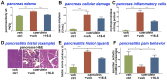
TRPV4 ion channels represent osmo-mechano-TRP channels with pleiotropic function and wide-spread expression. One of the critical functions of TRPV4 in this spectrum is its involvement in pain and inflammation. However, few small-molecule inhibitors of TRPV4 are available. Here we developed TRPV4-inhibitory molecules based on modifications of a known TRPV4-selective tool-compound, GSK205. We not only increased TRPV4-inhibitory potency, but surprisingly also generated two compounds that potently co-inhibit TRPA1, known to function as chemical sensor of noxious and irritant signaling. We demonstrate TRPV4 inhibition by these compounds in primary cells with known TRPV4 expression - articular chondrocytes and astrocytes. Importantly, our novel compounds attenuate pain behavior in a trigeminal irritant pain model that is known to rely on TRPV4 and TRPA1. Furthermore, our novel dual-channel blocker inhibited inflammation and pain-associated behavior in a model of acute pancreatitis - known to also rely on TRPV4 and TRPA1. Our results illustrate proof of a novel concept inherent in our prototype compounds of a drug that targets two functionally-related TRP channels, and thus can be used to combat isoforms of pain and inflammation in-vivo that involve more than one TRP channel. This approach could provide a novel paradigm for treating other relevant health conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Content as reported in this paper has been included in patent applications by the Duke University Office of Licensing and Ventures.
Figures
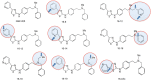
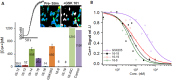
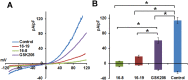
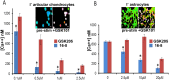
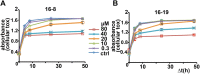
References
-
- Strotmann R., Harteneck C., Nunnenmacher K., Schultz G. & Plant T. D. OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol. 2, 695–702 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N., Joseph E., Dina O. A., Liedtke W. & Levine J. D. TRPV4 mediates pain-related behavior induced by mild hypertonic stimuli in the presence of inflammatory mediator. Pain 118, 70–79 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK091946/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F33 DE024668/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG046927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048182/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR050245/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015768/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064213/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA100639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098796/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DE022793/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018549/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

