XPA: A key scaffold for human nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 27247238
- PMCID: PMC4958585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.018
XPA: A key scaffold for human nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is essential for removing many types of DNA lesions from the genome, yet the mechanisms of NER in humans remain poorly understood. This review summarizes our current understanding of the structure, biochemistry, interaction partners, mechanisms, and disease-associated mutations of one of the critical NER proteins, XPA.
Keywords: DNA repair; NER; XPA; Xeroderma pigmentosum..
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


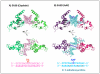

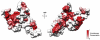

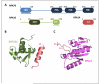

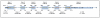
References
-
- Gillet LCJ, Scharer OD. Molecular Mechanisms of Mammalian Global Genome Nucleotide Excision Repair. Chem. Rev. 2006;106:253–276. - PubMed
-
- Truglio JJ, Croteau DL, Houten B. Van, Kisker C. Prokaryotic Nucleotide Excision Repair : The UvrABC System. 2006. - PubMed
-
- Hoeijmakers JHJ. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:1475–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

