Multidimensional structure-function relationships in human β-cardiac myosin from population-scale genetic variation
- PMID: 27247418
- PMCID: PMC4914177
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1606950113
Multidimensional structure-function relationships in human β-cardiac myosin from population-scale genetic variation
Abstract
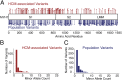
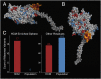
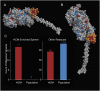
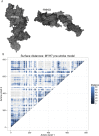
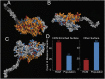
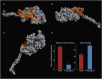
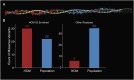
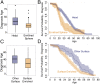
Myosin motors are the fundamental force-generating elements of muscle contraction. Variation in the human β-cardiac myosin heavy chain gene (MYH7) can lead to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a heritable disease characterized by cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death. How specific myosin variants alter motor function or clinical expression of disease remains incompletely understood. Here, we combine structural models of myosin from multiple stages of its chemomechanical cycle, exome sequencing data from two population cohorts of 60,706 and 42,930 individuals, and genetic and phenotypic data from 2,913 patients with HCM to identify regions of disease enrichment within β-cardiac myosin. We first developed computational models of the human β-cardiac myosin protein before and after the myosin power stroke. Then, using a spatial scan statistic modified to analyze genetic variation in protein 3D space, we found significant enrichment of disease-associated variants in the converter, a kinetic domain that transduces force from the catalytic domain to the lever arm to accomplish the power stroke. Focusing our analysis on surface-exposed residues, we identified a larger region significantly enriched for disease-associated variants that contains both the converter domain and residues on a single flat surface on the myosin head described as the myosin mesa. Notably, patients with HCM with variants in the enriched regions have earlier disease onset than patients who have HCM with variants elsewhere. Our study provides a model for integrating protein structure, large-scale genetic sequencing, and detailed phenotypic data to reveal insight into time-shifted protein structures and genetic disease.
Keywords: genetic burden; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; myosin; rare disease genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.A.S. is a founder of and owns shares in Cytokinetics, Inc. and MyoKardia, Inc., biotechnology companies that are developing therapeutics that target the sarcomere. E.M.G. is an employee and owns shares in MyoKardia, Inc. E.A.A. is a founder of Personalis, Inc. C.D.B. is on the Scientific Advisory Boards of
Figures

References
-
- Krendel M, Mooseker MS. Myosins: Tails (and heads) of functional diversity. Physiology (Bethesda) 2005;20:239–251. - PubMed
-
- Maron BJ, et al. Prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a general population of young adults. Echocardiographic analysis of 4111 subjects in the CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in (Young) Adults. Circulation. 1995;92(4):785–789. - PubMed
-
- Maron BJ, Casey SA, Hauser RG, Aeppli DM. Clinical course of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with survival to advanced age. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(5):882–888. - PubMed
-
- Walsh R, Rutland C, Thomas R, Loughna S. Cardiomyopathy: A systematic review of disease-causing mutations in myosin heavy chain 7 and their phenotypic manifestations. Cardiology. 2010;115(1):49–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

