Nigella sativa seed decreases endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat aorta
- PMID: 27247923
- PMCID: PMC4884219
Nigella sativa seed decreases endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat aorta
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes is an important risk factor for cardiovascular events. The great percent of morbidity in patients with diabetes is due to endothelial dysfunction. The present study investigated the effects of hydroalcholic extract of Nigella sativa (N. sativa) on contractile and dilatation response of isolated aorta in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat.
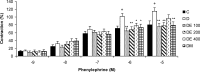
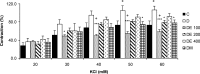
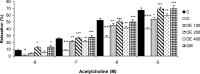
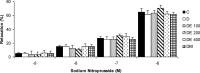
Materials and methods: Rats were divided into six experimental groups (control, untreated STZ-diabetic, and N. sativa hydroalcholic extract or metformin-treated diabetic rats). Treated rats received N. sativa extract (100, 200, and 400 mg/kg) or metformin (300 mg/kg) by gavage, daily for 6 weeks. Isolated rat thoracic rings were mounted in an organ bath system then contractile and dilatation responses induced by phenylephrine (PE), acetylcholine (ACh), potassium chloride (KCl), and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) were evaluated in different situations.
Results: The lower concentrations of N. sativa seed extract (DE 100 and DE 200) and metformin significantly reduced the contractile responses to higher concentrations of PE (10(-6) - 10(-5) M) compared to diabetic group (p<0.05 to p<0.01). The relaxation response to Ach 10(-8) M, was increased in DE 200 and metformin groups compared to diabetic group (p<0.05). The relaxation responses to Ach 10(-7) - 10(-5) M were significantly higher in all treated groups compared to diabetic group (p<0.05 to p<0.001).
Conclusion: Chronic administration of N. sativa seed extract has a significant hypoglycemic effect and improves aortic reactivity to vasoconstrictor and vasodilator agents in STZ-induced diabetic rats.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Endothelial dysfunction; Isolated aorta; Nigella sativa; Rat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nigella sativa L. seed regulated eNOS, VCAM-1 and LOX-1 genes expression and improved vasoreactivity in aorta of diabetic rat.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jan 10;228:142-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.021. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30223051
-
The effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Nigella sativa seed on oxidative stress in hippocampus of STZ-induced diabetic rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015 Jul-Aug;5(4):333-40. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015. PMID: 26445713 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, restores endothelial function in aorta of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Apr 1;66(1):150-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.025. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15769458
-
Metformin reduces blood pressure and restores endothelial function in aorta of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Life Sci. 2006 Apr 25;78(22):2615-24. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.10.020. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16318863
-
Antioxidant and triglyceride-lowering effects of vitamin E associated with the prevention of abnormalities in the reactivity and morphology of aorta from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Antioxidants in Diabetes-Induced Complications (ADIC) Study Group.Metabolism. 1997 Aug;46(8):872-9. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90072-x. Metabolism. 1997. PMID: 9258267
Cited by
-
Protective effects of wheat germ oil against erectile and endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Int J Impot Res. 2022 Sep;34(6):581-587. doi: 10.1038/s41443-021-00453-4. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Impot Res. 2022. PMID: 34108653
-
Comparison of the Neuroprotective Effects of Aspirin, Atorvastatin, Captopril and Metformin in Diabetes Mellitus.Biomolecules. 2019 Mar 27;9(4):118. doi: 10.3390/biom9040118. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30934759 Free PMC article.
-
A nutraceutical combination of Cinnamomum cassia &Nigella sativa for Type 1 diabetes mellitus.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2018 Jan-Mar;9(1):27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 28988684 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin Promotes Wound Healing by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Metformin-Controlled Diabetes in Rats.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 13;9(30):32394-32406. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05595. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39100330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abebe W, Harris KH, Macleod KM. Enhanced contractile responses of arteries from diabetic rats to alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation in the absence and presence of extracellular calcium. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;16:239–248. - PubMed
-
- Calvert JW, Gundewar S, Jha S, Greer JJ, Bestermann WH, Tian R, Lefer DJ. Acute metformin therapy confers cardioprotection against myocardial infarction via AMPK-eNOS-mediated signaling. Diabetes. 2008;57:696–705. - PubMed
-
- Capellini VK, Baldo CF, Celotto AC, Batalhao ME, Carnio EC, Rodrigues AJ, Evora PR. Oxidative stress is not associated with vascular dysfunction in a model of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2010;54:530–539. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
