Plant synthetic biology for molecular engineering of signalling and development
- PMID: 27249346
- PMCID: PMC5164986
- DOI: 10.1038/nplants.2016.10
Plant synthetic biology for molecular engineering of signalling and development
Abstract
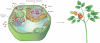
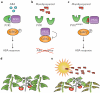
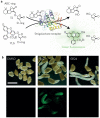
Molecular genetic studies of model plants in the past few decades have identified many key genes and pathways controlling development, metabolism and environmental responses. Recent technological and informatics advances have led to unprecedented volumes of data that may uncover underlying principles of plants as biological systems. The newly emerged discipline of synthetic biology and related molecular engineering approaches is built on this strong foundation. Today, plant regulatory pathways can be reconstituted in heterologous organisms to identify and manipulate parameters influencing signalling outputs. Moreover, regulatory circuits that include receptors, ligands, signal transduction components, epigenetic machinery and molecular motors can be engineered and introduced into plants to create novel traits in a predictive manner. Here, we provide a brief history of plant synthetic biology and significant recent examples of this approach, focusing on how knowledge generated by the reference plant Arabidopsis thaliana has contributed to the rapid rise of this new discipline, and discuss potential future directions.
Figures

References
-
- The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Medford JI, Prasad A. Plant synthetic biology takes root. Science. 2014;346:162–163. - PubMed
-
- Purnick PE, Weiss R. The second wave of synthetic biology: from modules to systems. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:410–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

