Non-coding RNAs in muscle differentiation and musculoskeletal disease
- PMID: 27249675
- PMCID: PMC4887180
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI84419
Non-coding RNAs in muscle differentiation and musculoskeletal disease
Abstract
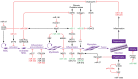
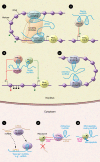
RNA is likely to be the most rediscovered macromolecule in biology. Periodically, new non-canonical functions have been ascribed to RNA, such as the ability to act as a catalytic molecule or to work independently from its coding capacity. Recent annotations show that more than half of the transcriptome encodes for RNA molecules lacking coding activity. Here we illustrate how these transcripts affect skeletal muscle differentiation and related disorders. We discuss the most recent scientific discoveries that have led to the identification of the molecular circuitries that are controlled by RNA during the differentiation process and that, when deregulated, lead to pathogenic events. These findings will provide insights that can aid in the development of new therapeutic interventions for muscle diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(suppl 1):R17–R29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

