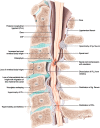
Degenerative cervical myelopathy
- PMID: 27250040
- PMCID: PMC4958380
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-016-9348-5
Degenerative cervical myelopathy
Abstract
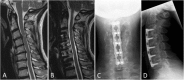
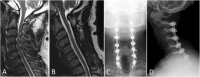
Cervical myelopathy is the most common cause of acquired spinal cord compromise. The concept of degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM), defined as symptomatic myelopathy associated with degenerative arthropathic changes in the spine axis, is being introduced. Given its progressive nature, treatment options have to be chosen in a timely manner. Surgical options include anterior discectomy and fusion (ACDF), anterior corpectomy and fusion (ACCF), arthroplasty (in highly select cases), posterior laminectomy with/without fusion, and laminoplasty. Indications for each should be carefully considered in individual patients. Riluzole, a sodium-glutamate antagonist, is a promising option to optimize neurologic outcomes post-surgery and is being examined in the CSM-Protect Randomized Controlled Trial. Preoperative risk assessment is mandatory for prognostication. Sagittal alignment is known to play an important role to optimize surgical outcome. Guidelines for optimal management of DCM are in process. In principle, all but the mildest cases of DCM should be offered surgery for optimal outcome.
Keywords: Adjuvant therapy; Approach; Degenerative cervical myelopathy; Non-surgical treatment; Prognosis; Surgical treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Nouri A, Tetreault L, Singh A, et al. Degenerative cervical myelopathy: epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40:E675–93. Recent narrative review introducing degenerative cervical myelopathy with its detailed description. - PubMed
-
- Rhee JM, Shamji MF, Erwin WM, et al. Nonoperative management of cervical myelopathy: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38:S55–67. Systematic review of evidences regarding nonoperative treatment of cervical myelopathy. They concluded nonoperative treatment is not routinely recommended given the paucity of evidence. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

