Giant Seebeck effect in Ge-doped SnSe
- PMID: 27251233
- PMCID: PMC4890000
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26774
Giant Seebeck effect in Ge-doped SnSe
Abstract
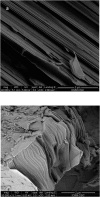
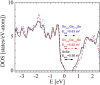
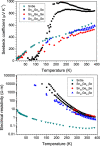
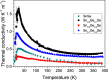
Thermoelectric materials may contribute in the near future as new alternative sources of sustainable energy. Unprecedented thermoelectric properties in p-type SnSe single crystals have been recently reported, accompanied by extremely low thermal conductivity in polycrystalline samples. In order to enhance thermoelectric efficiency through proper tuning of this material we report a full structural characterization and evaluation of the thermoelectric properties of novel Ge-doped SnSe prepared by a straightforward arc-melting method, which yields nanostructured polycrystalline samples. Ge does not dope the system in the sense of donating carriers, yet the electrical properties show a semiconductor behavior with resistivity values higher than that of the parent compound, as a consequence of nanostructuration, whereas the Seebeck coefficient is higher and thermal conductivity lower, favorable to a better ZT figure of merit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
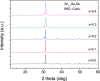
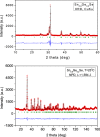
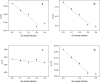
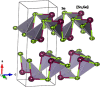
References
-
- Goldsmid. H. J. Thermoelectric Refrigeration. (Temple Press Books, Ltd., 1964).
-
- Rowe D. M. (ed). Thermoelectrics and Its Energy Harvesting. (CRC press, 2012).
-
- Bell L. E. Cooling, heating, generating power, and recovering waste heat with thermoelectric systems. Science 321, 1457–1461 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Zhao L.-D., Dravid V. P. & Kanatzidis M. G. The panoscopic approach to high performance thermoelectrics. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 251–268 (2014).
-
- Snyder G. J. & Toberer E. S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 7, 105–114 (2008). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

