Epidemiological characteristics of human prion diseases
- PMID: 27251305
- PMCID: PMC4890484
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-016-0143-8
Epidemiological characteristics of human prion diseases
Abstract
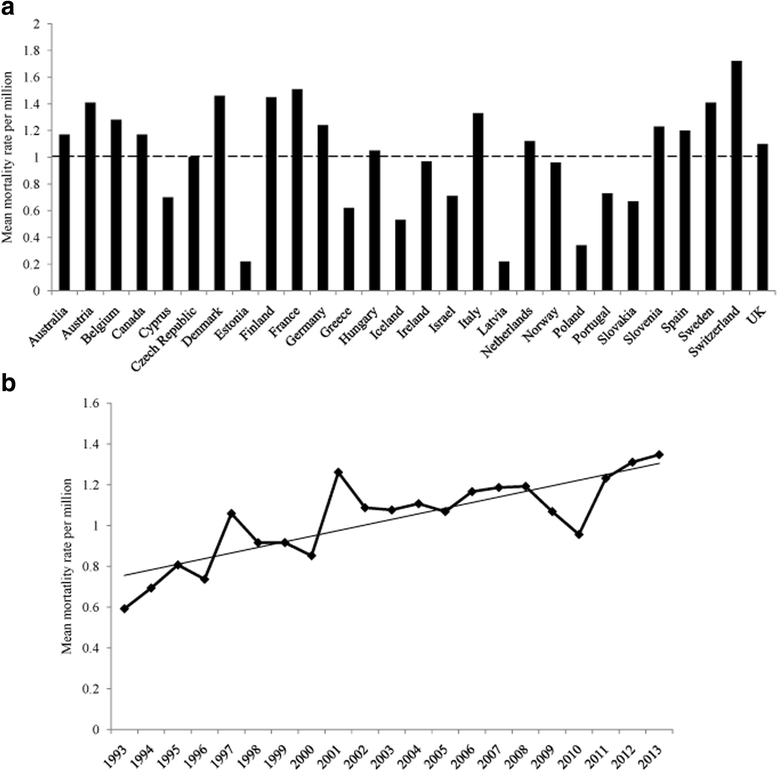
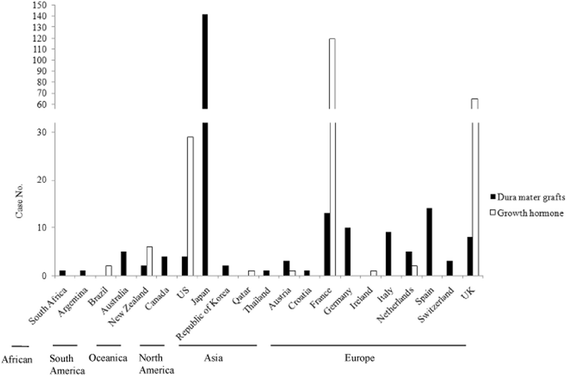
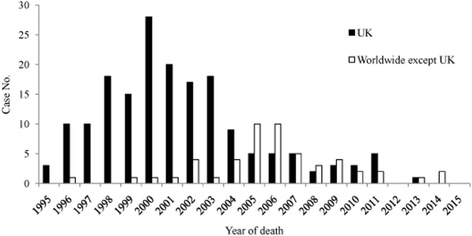
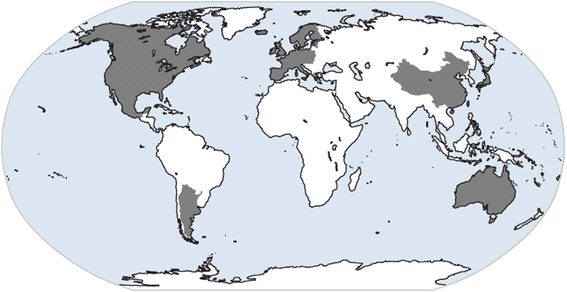
Human prion diseases are a group of transmissible, progressive, and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disorders, which include Kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome, and fatal familial insomnia. Human prion diseases affect approximately 1-2 persons per million worldwide annually, occurring in sporadic, inherited, and acquired forms. These diseases have attracted both scientific and public attention not only because of their mysterious pathogen, but also due to their considerable threat to public health since the emergence of the variant CJD.There are still no specific therapeutic and prophylactic interventions available for prion diseases, thus active surveillance of human prion diseases is critical for disease control and prevention. Since 1993, CJD surveillance systems have been established in many countries and regions, and several long-term multinational cooperative projects have been conducted.In this paper, the epidemiological characteristics of various human prion diseases and the active surveillance systems pertaining to them in different countries and regions are summarized and reviewed.
Keywords: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; Epidemiology; Prion disease; Surveillance.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

