Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
- PMID: 27252362
- PMCID: PMC4888821
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021899
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
Abstract
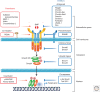
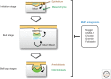
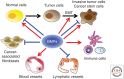
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), originally identified as osteoinductive components in extracts derived from bone, are now known to play important roles in a wide array of processes during formation and maintenance of various organs including bone, cartilage, muscle, kidney, and blood vessels. BMPs and the related "growth and differentiation factors" (GDFs) are members of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family, and transduce their signals through type I and type II serine-threonine kinase receptors and their intracellular downstream effectors, including Smad proteins. Furthermore, BMP signals are finely tuned by various agonists and antagonists. Because deregulation of the BMP activity at multiple steps in signal transduction is linked to a wide variety of human diseases, therapeutic use of activators and inhibitors of BMP signaling will provide potential avenues for the treatment of the human disorders that are caused by hypo- and hyperactivation of BMP signals, respectively.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama S, Katagiri T, Namiki M, Yamaji N, Yamamoto N, Miyama K, Shibuya H, Ueno N, Wozney JM, Suda T. 1997. Constitutively active BMP type I receptors transduce BMP-2 signals without the ligand in C2C12 myoblasts. Exp Cell Res 235: 362–369. - PubMed
-
- Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. 2010. Bone morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer: Dual role in tumourigenesis? Endocr Relat Cancer 17: 123–139. - PubMed
-
- Alarmo EL, Korhonen T, Kuukasjärvi T, Huhtala H, Holli K, Kallioniemi A. 2008. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 expression associates with bone metastasis in breast carcinomas. Ann Oncol 19: 308–314. - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. 2004. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development 131: 2257–2268. - PubMed
-
- Asahina I, Sampath TK, Haushka PV. 1996. Human osteogenic protein-1 induces chondrogenic, osteoblastic, and/or adipogenic differentiation of clonal murine target cells. Exp Cell Res 222: 38–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
