Identification of a Noroxomaritidine Reductase with Amaryllidaceae Alkaloid Biosynthesis Related Activities
- PMID: 27252378
- PMCID: PMC4974387
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.717827
Identification of a Noroxomaritidine Reductase with Amaryllidaceae Alkaloid Biosynthesis Related Activities
Abstract
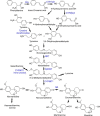
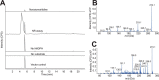
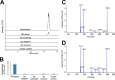
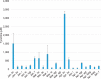
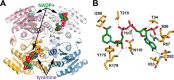
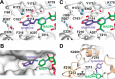
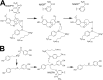
Amaryllidaceae alkaloids are a large group of plant natural products with over 300 documented structures and diverse biological activities. Several groups of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids including the hemanthamine- and crinine-type alkaloids show promise as anticancer agents. Two reduction reactions are required for the production of these compounds: the reduction of norcraugsodine to norbelladine and the reduction of noroxomaritidine to normaritidine, with the enantiomer of noroxomaritidine dictating whether the derivatives will be the crinine-type or hemanthamine-type. It is also possible for the carbon-carbon double bond of noroxomaritidine to be reduced, forming the precursor for maritinamine or elwesine depending on the enantiomer reduced to an oxomaritinamine product. In this study, a short chain alcohol dehydrogenase/reductase that co-expresses with the previously discovered norbelladine 4'-O-methyltransferase from Narcissus sp. and Galanthus spp. was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli Biochemical analyses and x-ray crystallography indicates that this protein functions as a noroxomaritidine reductase that forms oxomaritinamine from noroxomaritidine through a carbon-carbon double bond reduction. The enzyme also reduces norcraugsodine to norbelladine with a 400-fold lower specific activity. These studies identify a missing step in the biosynthesis of this pharmacologically important class of plant natural products.
Keywords: Amaryllidaceae alkaloids; crystal structure; enzyme structure; norbelladine; noroxomaritidine reductase; reductase; secondary metabolism; transcriptomics.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


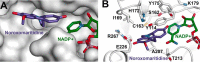
References
-
- Wilcock G., Howe I., Coles H., Lilienfeld S., Truyen L., Zhu Y., Bullock R., Kershaw P., and Group G.-G.-S. (2003) A long-term comparison of galantamine and donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Drugs Aging 20, 777–789 - PubMed
-
- Havelek R., Seifrtova M., Kralovec K., Bruckova L., Cahlikova L., Dalecka M., Vavrova J., Rezacova M., Opletal L., and Bilkova Z. (2014) The effect of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids haemanthamine and haemanthidine on cell cycle progression and apoptosis in p53-negative human leukemic Jurkat cells. Phytomedicine 21, 479–490 - PubMed
-
- He M., Qu C., Gao O., Hu X., and Hong X. (2015) Biological and pharmacological activities of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. R.S.C. Adv. 5, 16562–16574
-
- Lamoral-Theys D., Andolfi A., Van Goietsenoven G., Cimmino A., Le Calvé B., Wauthoz N., Mégalizzi V., Gras T., Bruyère C., Dubois J., Mathieu V., Kornienko A., Kiss R., and Evidente A. (2009) Lycorine, the main phenanthridine Amaryllidaceae alkaloid, exhibits significant antitumor activity in cancer cells that display resistance to proapoptotic stimuli: an investigation of structure-activity relationship and mechanistic insight. J. Med. Chem. 52, 6244–6256 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Halim O. B., Morikawa T., Ando S., Matsuda H., and Yoshikawa M. (2004) New crinine-type alkaloids with inhibitory effect on induction of inducible nitric-oxide synthase from Crinum yemense. J. Nat. Prod. 67, 1119–1124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

