Transport of Calcium Ions into Mitochondria
- PMID: 27252588
- PMCID: PMC4869008
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202917666160202215748
Transport of Calcium Ions into Mitochondria
Abstract
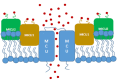
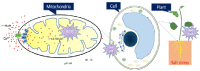
To uptake calcium ions of mitochondria is of significant functional connotation for cells, because calcium ions in mitochondria are involved in energy production, regulatory signals transfer, and mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening and even programmed cell death of apoptosis, further playing more roles in plant productivity and quality. Cytoplasmic calcium ions access into outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) from voltage dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) and were absorbed into inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) by mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU), rapid mitochondrial calcium uptake (RaM) or mitochondrial ryanodine receptor (mRyR). Although both mitochondria and the mechanisms of calcium transport have been extensively studied, but there are still long-standing or even new challenges. Here we review the history and recent discoveries of the mitochondria calcium ions channel complex involved calcium assimilation, and discuss the role of calcium ions into mitochondria.
Keywords: Calcium ions uptake; Channels; Mitochondria; Uniporter..
Figures
References
-
- Rossi C.S., Lehninger A.L. Stoichiometry of respiratory stimulation, accumulation of Ca2+ and phosphate, and oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1964;239(11):3971–3980. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
