Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation in Urinary Tract Infection
- PMID: 27252918
- PMCID: PMC4888176
Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation in Urinary Tract Infection
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the antibiotic susceptibility pattern as well as the phenotypic and genotypic biofilm formation ability of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with urinary tract infection (UTI).
Methods: A total of 39 isolates of S. aureus were collected from patients with UTI. The antibiotic susceptibility patterns of the isolates were determined by the Kirby-Bauer disk-diffusion. We used the Modified Congo red agar (MCRA) and Microtiter plate methods to assess the ability of biofilm formation. All isolates were examined for determination of biofilm related genes, icaA, fnbA, clfA and bap using PCR method.
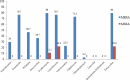
Results: Linezolid, quinupristin/dalfopristin and chloramphenicol were the most effective agents against S. aureus isolates. Overall, 69.2% of S. aureus isolates were biofilm producers. Resistance to four antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin (71.4% vs. 28.6%, P=0.001), tetracycline (57.7% vs. 42.3%, P=0.028), erythromycin and ciprofloxacin (56% vs. 44%, P=0.017) was higher among biofilm producers than non-biofilm producers. The icaA, fnbA and clfA genes were present in all S. aureus isolates. However, bap gene was not detected in any of the isolates.
Conclusion: Our findings reinforce the role of biofilm formation in resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole and doxycycline may be used as an effective treatment for UTI caused by biofilm producers S. aureus. Our results suggest that biofilm formation is not dependent to just icaA, fnbA, clfA and bap genes harbor in S. aureus strains.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Biofilm formation; Staphylococcus aureus; Urinary tract infection.
Figures


References
-
- Ranjbar R, Haghi-Ashtiani M, Jafari NJ, Abedini M. (2009). The prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial uropathogens isolated from pediatric patients. Iran J Public Health, 38 ( 2): 134–38.
-
- Mobaleghi J, Salimizand H, Beiranvand S, Membari Sh, Kalantar E. (2012). Extended spectrum beta-lactamases in urinary isolates of Escherichia coli in five Iranian hospitals. Int J Infect Dis, 5: 35–6.
-
- Kayas L, Yolbas I, Ece A, Kayas Y, Kocamaz H. (2011). Causative agents and antibiotic susceptibilities in children with urinary tract infection. J Microbiol Infect Dis, 1 ( 101): 17–21.
-
- Tayebi Z, Seyedjavadi SS, Goudarzi M, Rahimi MK, Boromandi S, Bostanabad SZ. (2014). Frequency and antibiotic resistance pattern in gram positive uropathogenes isolated from hospitalized patients with urinary tract infection in Tehran, Iran. J Genes Microb Immun, 1 – 9 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
