Role of long non-coding RNA-RNCR3 in atherosclerosis-related vascular dysfunction
- PMID: 27253412
- PMCID: PMC5143375
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.145
Role of long non-coding RNA-RNCR3 in atherosclerosis-related vascular dysfunction
Abstract
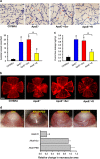
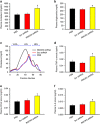
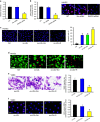
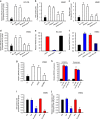
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common vascular disorders. Endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction and vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in several biological processes and human diseases. Here we show that lncRNA-RNCR3 is expressed in ECs and VSMCs. RNCR3 expression is significantly upregulated in mouse and human aortic atherosclerotic lesions, and cultured ECs and VSMCs upon ox-LDL treatment in vitro. RNCR3 knockdown accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, aggravates hypercholesterolemia and inflammatory factor releases, and decreases EC and VSMC proliferation in vivo. RNCR3 knockdown also reduces the proliferation and migration, and accelerates apoptosis development of EC and VSMC in vitro. RNCR3 acts as a ceRNA, and forms a feedback loop with Kruppel-like factor 2 and miR-185-5p to regulate cell function. This study reveals that RNCR3 has an atheroprotective role in atherosclerosis, and its intervention is a promising strategy for treating atherosclerosis-related vascular dysfunction.
Figures



References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011; 473: 317–325. - PubMed
-
- Verweij SL, van der Valk FM, Stroes ES. Novel directions in inflammation as a therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol 2015; 26: 580–585. - PubMed
-
- Loyer X, Potteaux S, Vion A-C, Guérin CL, Boulkroun S, Rautou P-E et al. Inhibition of microRNA-92a prevents endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in mice. Circ Res 2014; 114: 434–443. - PubMed
-
- Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Singh KK, Shukla PC, Gupta N et al. MicroRNA-145 targeted therapy reduces atherosclerosis. Circulation 2012; 126: S81–S90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

