New advances in invasive aspergillosis immunobiology leading the way towards personalized therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 27253487
- PMCID: PMC4904826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.05.015
New advances in invasive aspergillosis immunobiology leading the way towards personalized therapeutic approaches
Abstract
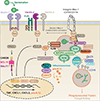
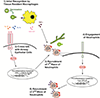
Invasive aspergillosis (IA) remains a devastating disease in immune compromised patients despite significant advances in our understanding of fungal virulence and host defense mechanisms. In this review, we summarize important research advances in the fight against IA with particular focus on early events in the interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and the host that occur in the respiratory tract. Advances in understanding mechanisms of immune effector cell recruitment, antifungal effector mechanisms, and how the dynamic host-fungal interaction alters the local microenvironment to effect outcomes are highlighted. These advances illustrate exciting new therapeutic opportunities, but also emphasize the importance of understanding each unique fungus-host interaction for improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Antifungal effector; Aspergillus fumigatus; Fungal virulence; Invasive aspergillosis; Phagocytes.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of hypoxic microenvironments during invasive aspergillosis.Med Mycol. 2011 Apr;49 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S120-4. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2010.495139. Epub 2010 Jun 21. Med Mycol. 2011. PMID: 20560863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into invasive aspergillosis--from the pathogen to the disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(20):3679-88. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990366. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23278533 Review.
-
Immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus in compromised hosts: from bedside to bench.Future Microbiol. 2011 Jan;6(1):73-83. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.158. Future Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21162637 Review.
-
The Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus, Host Defense Mechanisms, and the Development of AFMP4 Antigen as a Vaccine.Pol J Microbiol. 2021 Mar;70(1):3-11. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2021-003. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Pol J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33815522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019 Nov 13;33(1):e00140-18. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00140-18. Print 2019 Dec 18. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31722890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detailed characterisation of invasive aspergillosis in a murine model of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease shows new insights in infections caused by Aspergillus fumigatus versus Aspergillus nidulans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Sep 1;13:1241770. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1241770. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37724291 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Pathogens: Shape-Shifting Invaders.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Nov;28(11):922-933. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 27. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32474010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host-Derived Leukotriene B4 Is Critical for Resistance against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 11;8:1984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01984. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29375586 Free PMC article.
-
From phagocytosis to metaforosis: Calcineurin's deadly role in innate processing of fungi.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jan 4;14(1):e1006627. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006627. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29300778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interleukin 1α Is Critical for Resistance against Highly Virulent Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates.Infect Immun. 2017 Nov 17;85(12):e00661-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00661-17. Print 2017 Dec. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28947643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aimanianda V, Bayry J, Bozza S, Kniemeyer O, Perruccio K, Elluru SR, Clavaud C, Paris S, Brakhage AA, Kaveri SV, Romani L, Latge JP. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature. 2009;460:1117–1121. - PubMed
-
- Akoumianaki T, Kyrmizi I, Valsecchi I, Gresnigt MS, Samonis G, Drakos E, Boumpas D, Muszkieta L, Prevost MC, Kontoyiannis DP, Chavakis T, Netea MG, van de Veerdonk FL, Brakhage AA, El-Benna J, Beauvais A, Latge JP, Chamilos G. Aspergillus Cell Wall Melanin Blocks LC3-Associated Phagocytosis to Promote Pathogenicity. Cell host & microbe. 2016;19:79–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

