Prognostic significance of synergistic hexokinase-2 and beta2-adrenergic receptor expression in human hepatocelluar carcinoma after curative resection
- PMID: 27255554
- PMCID: PMC4891884
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-016-0474-8
Prognostic significance of synergistic hexokinase-2 and beta2-adrenergic receptor expression in human hepatocelluar carcinoma after curative resection
Abstract
Background: Hexokinase-2 (HK2) and Beta2-adrenergic receptor (Beta2AR) are overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and associated with poor prognosis. However, the synergistic effect of HK2 and Beta2AR in HCC prognosis is not elucidated. The present study aims to investigate the association between HK2 and Beta2AR expressions in HCC tissues, and to evaluate the synergistic effect of HK2 and Beta2AR in HCC prognosis.
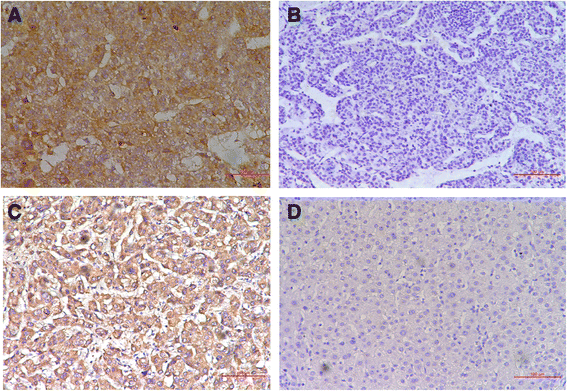
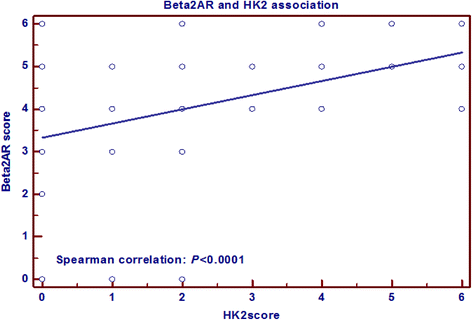
Methods: Immunohistochemistry of HK2 and Beta2AR was performed on 155 paraffin embedded HCC samples retrieved from the archives of pathology department. Corresponding clinical data and prognostic data were collected through searching medical record systems, death registration systems and interviews with patient families. Spearman correlation test was performed to evaluate the association between HK2 and Beta2AR expression. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and Cox regressions were employed to evaluate HK2 and Beta2AR expression in HCC prognosis, respectively and synergistically.
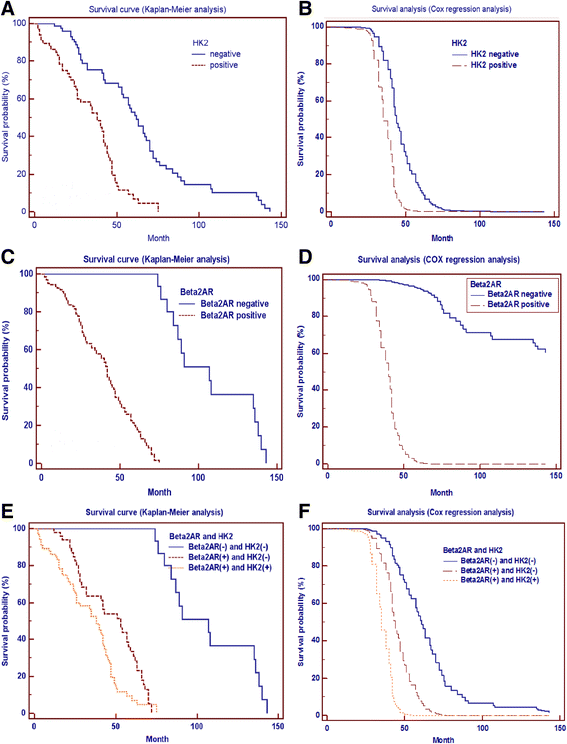
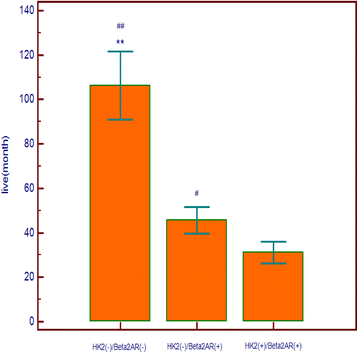
Results: 109 of 155 HCC patients reached the death point, the survival time of HCC patients was 46.23 ± 31.01 months after curative surgical resections of HCC. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that large tumor size (more than 5 cm) (hazard ratio (HR) = 8.42, 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 3.81-18.59, P < 0.0001), advanced TNM stage (III and IV stages) (HR = 2.09, 95%CI = 1.21-3.62, P < 0.001) and AFP more than 20 μg/L (HR = 1.49, 95%CI = 1.02-2.18, P = 0.0302) were predictors for poor prognosis. HK2 and Beta2AR positive expression was detected in 66 (42.58) and 122 (78.71 %) HCC samples respectively. In univariate analysis, HK2(+) (HR = 2.70, 95%CI = 1.76-4.15, P < 0.0001) and Beta2AR(+) (HR = 4.61, 96%CI = 3.14-6.76, P < 0.0001) were associated with poor prognosis. In multivariate analysis, HK2(+) (P < 0.0001) and Beta2AR(+) (P < 0.0001) were also associated with poor prognosis. HK2(+)/Beta2AR(+) in HCC samples had poorer prognosis compared with HK2(-)/Beta2AR(-) in both univariate analysis (HR = 4.69, 95%CI = 2.91-7.57, P < 0.0001) and multivariate analysis (P < 0.0001). HK2(+)/Beta2AR(+) in HCC samples had poorer prognosis compared with HK2(-)/Beta2AR(+) in both univariate analysis (HR = 1.76, 95%CI = 1.17-2.64, P = 0.003) and multivariate analysis (P = 0.004).
Conclusion: HK2 and Beta2AR play important roles in HCC progression. HK2 and Beta2AR expression in HCC is correlated positively. Beta2AR may increase HCC invasion and metastasis in collaboration with HK2. HK2 and Beta2AR can predict HCC prognosis both independently and synergistically.
Keywords: Beta2-adrenergic receptor; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Hexokinase-2; Immunohistochemistry; Prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The beta2-adrenergic receptor is a potential prognostic biomarker for human hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Oct;19(11):3556-65. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2396-1. Epub 2012 May 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22588469
-
Neuron-glial antigen 2 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poor prognosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 7;21(21):6649-59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6649. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26074703 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2012 Sep;65(9):808-14. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200721. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22734007
-
Poor prognosis of hexokinase 2 overexpression in solid tumors of digestive system: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(19):32332-32344. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15974. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical significance of microRNA-122 in predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis validated by the Cancer Genome Atlas dataset.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(13):e14810. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014810. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30921182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of HK2, PKM2 and LDHA on Cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5553-5560. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8005. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552193 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 May 6;22(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03396-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38711095 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of the Metabolic Marker Hexokinase-2 in Various Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 8;11(11):e0166230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166230. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27824926 Free PMC article.
-
SPI1 involvement in malignant melanoma pathogenesis by regulation of HK2 through the AKT1/mTOR pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(18):2675-2683. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17844. Epub 2023 Aug 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37539493 Free PMC article.
-
Propranolol suppresses the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of liver cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5213-5221. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8476. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cainap C, Qin S, Huang WT, Chung IJ, Pan H, Cheng Y, Kudo M, Kang YK, Chen PJ, Toh HC, Gorbunova V, Eskens FA, Qian J, McKee MD, Ricker JL, Carlson DM, El-Nowiem S. Linifanib versus Sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(2):172–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.3298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maudsley S, Pierce KL, Zamah AM, Miller WE, Ahn S, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ, Luttrell LM. The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via assembly of a multireceptor complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:9572–80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.13.9572. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

