Quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic structures with subnanometre gaps
- PMID: 27255556
- PMCID: PMC4895716
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11495
Quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic structures with subnanometre gaps
Abstract
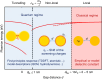
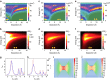
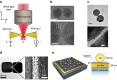
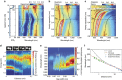
Metallic structures with nanogap features have proven highly effective as building blocks for plasmonic systems, as they can provide a wide tuning range of operating frequencies and large near-field enhancements. Recent work has shown that quantum mechanical effects such as electron tunnelling and nonlocal screening become important as the gap distances approach the subnanometre length-scale. Such quantum effects challenge the classical picture of nanogap plasmons and have stimulated a number of theoretical and experimental studies. This review outlines the findings of many groups into quantum mechanical effects in nanogap plasmons, and discusses outstanding challenges and future directions.
Figures
References
-
- Maier S. A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications Springer (2007).
-
- Halas N. J. Plasmonics: an emerging field fostered by Nano Letters. Nano Lett. 10, 3816–3822 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Hao E. & Schatz G. C. Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J. Chem. Phys. 120, 357–366 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Crozier K. B., Sundaramurthy A., Kino G. S. & Quate C. F. Optical antennas: Resonators for local field enhancement. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 4632–4642 (2003).
-
- Yu N. et al.. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334, 333–337 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

