Short Term Palmitate Supply Impairs Intestinal Insulin Signaling via Ceramide Production
- PMID: 27255710
- PMCID: PMC4965580
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.709626
Short Term Palmitate Supply Impairs Intestinal Insulin Signaling via Ceramide Production
Abstract
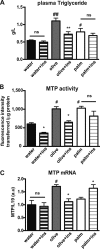
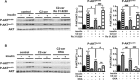
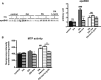
The worldwide prevalence of metabolic diseases is increasing, and there are global recommendations to limit consumption of certain nutrients, especially saturated lipids. Insulin resistance, a common trait occurring in obesity and type 2 diabetes, is associated with intestinal lipoprotein overproduction. However, the mechanisms by which the intestine develops insulin resistance in response to lipid overload remain unknown. Here, we show that insulin inhibits triglyceride secretion and intestinal microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression in vivo in healthy mice force-fed monounsaturated fatty acid-rich olive oil but not in mice force-fed saturated fatty acid-rich palm oil. Moreover, when mouse intestine and human Caco-2/TC7 enterocytes were treated with the saturated fatty acid, palmitic acid, the insulin-signaling pathway was impaired. We show that palmitic acid or palm oil increases ceramide production in intestinal cells and that treatment with a ceramide analogue partially reproduces the effects of palmitic acid on insulin signaling. In Caco-2/TC7 enterocytes, ceramide effects on insulin-dependent AKT phosphorylation are mediated by protein kinase C but not by protein phosphatase 2A. Finally, inhibiting de novo ceramide synthesis improves the response of palmitic acid-treated Caco-2/TC7 enterocytes to insulin. These results demonstrate that a palmitic acid-ceramide pathway accounts for impaired intestinal insulin sensitivity, which occurs within several hours following initial lipid exposure.
Keywords: Akt PKB; ceramide; fatty acid; insulin; intestine; lipid; palmitic acid; signaling.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Bansal S., Buring J. E., Rifai N., Mora S., Sacks F. M., and Ridker P. M. (2007) Fasting compared with nonfasting triglycerides and risk of cardiovascular events in women. JAMA 298, 309–316 - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard B. G., Benn M., Schnohr P., and Tybjaerg-Hansen A. (2007) Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA 298, 299–308 - PubMed
-
- Duez H., Pavlic M., and Lewis G. F. (2008) Mechanism of intestinal lipoprotein overproduction in insulin resistant humans. Atherosclerosis 9, 33–38 - PubMed
-
- Adeli K., and Lewis G. F. (2008) Intestinal lipoprotein overproduction in insulin-resistant states. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 19, 221–228 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

