Using metabarcoding to reveal and quantify plant-pollinator interactions
- PMID: 27255732
- PMCID: PMC4891682
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27282
Using metabarcoding to reveal and quantify plant-pollinator interactions
Abstract
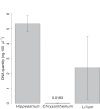
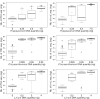
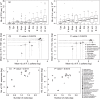
Given the ongoing decline of both pollinators and plants, it is crucial to implement effective methods to describe complex pollination networks across time and space in a comprehensive and high-throughput way. Here we tested if metabarcoding may circumvent the limits of conventional methodologies in detecting and quantifying plant-pollinator interactions. Metabarcoding experiments on pollen DNA mixtures described a positive relationship between the amounts of DNA from focal species and the number of trnL and ITS1 sequences yielded. The study of pollen loads of insects captured in plant communities revealed that as compared to the observation of visits, metabarcoding revealed 2.5 times more plant species involved in plant-pollinator interactions. We further observed a tight positive relationship between the pollen-carrying capacities of insect taxa and the number of trnL and ITS1 sequences. The number of visits received per plant species also positively correlated to the number of their ITS1 and trnL sequences in insect pollen loads. By revealing interactions hard to observe otherwise, metabarcoding significantly enlarges the spatiotemporal observation window of pollination interactions. By providing new qualitative and quantitative information, metabarcoding holds great promise for investigating diverse facets of interactions and will provide a new perception of pollination networks as a whole.
Conflict of interest statement
P.T. is co-inventor of patents related to the gh primers and the use of the P6 loop of the chloroplast trnL (UAA) intron for plant identification using degraded template DNA. These patents only restrict commercial applications and have no impact on the use of this locus by academic researchers.
Figures
References
-
- Biesmeijer J. C. et al. Parallel declines in pollinators and insect-pollinated plants in Britain and the Netherlands. Science 313, 351–354 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Goulson D. Effects of introduced bees on native ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34, 1–26 (2003).
-
- Bascompte J. & Jordano P. Plant-animal mutualistic networks: the architecture of biodiversity. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38, 567–593 (2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

