Severe hypoxemia: which strategy to choose
- PMID: 27255913
- PMCID: PMC4891828
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1304-7
Severe hypoxemia: which strategy to choose
Abstract
Background: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by a noncardiogenic pulmonary edema with bilateral chest X-ray opacities and reduction in lung compliance, and the hallmark of the syndrome is hypoxemia refractory to oxygen therapy. Severe hypoxemia (PaO2/FiO2 < 100 mmHg), which defines severe ARDS, can be found in 20-30 % of the patients and is associated with the highest mortality rate. Although the standard supportive treatment remains mechanical ventilation (noninvasive and invasive), possible adjuvant therapies can be considered. We performed an up-to-date clinical review of the possible available strategies for ARDS patients with severe hypoxemia.
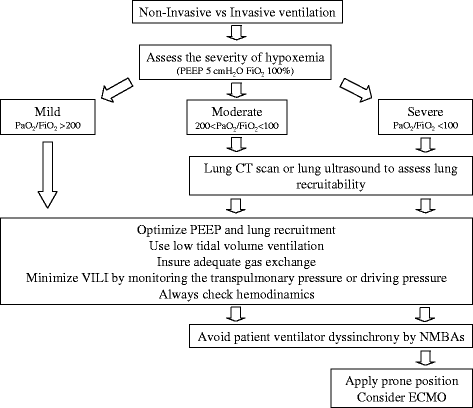
Main results: In summary, in moderate-to-severe ARDS or in the presence of other organ failure, noninvasive ventilatory support presents a high risk of failure: in those cases the risk/benefit of delayed mechanical ventilation should be evaluated carefully. Tailoring mechanical ventilation to the individual patient is fundamental to reduce the risk of ventilation-induced lung injury (VILI): it is mandatory to apply a low tidal volume, while the optimal level of positive end-expiratory pressure should be selected after a stratification of the severity of the disease, also taking into account lung recruitability; monitoring transpulmonary pressure or airway driving pressure can help to avoid lung overstress. Targeting oxygenation of 88-92 % and tolerating a moderate level of hypercapnia are a safe choice. Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) are useful to maintain patient-ventilation synchrony in the first hours; prone positioning improves oxygenation in most cases and promotes a more homogeneous distribution of ventilation, reducing the risk of VILI; both treatments, also in combination, are associated with an improvement in outcome if applied in the acute phase in the most severe cases. The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in severe ARDS is increasing worldwide, but because of a lack of randomized trials is still considered a rescue therapy.
Conclusion: Severe ARDS patients should receive a holistic framework of respiratory and hemodynamic support aimed to ensure adequate gas exchange while minimizing the risk of VILI, by promoting lung recruitment and setting protective mechanical ventilation. In the most severe cases, NMBAs, prone positioning, and ECMO should be considered.
Figures
References
-
- Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, Fan E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307:2526–33. - PubMed
-
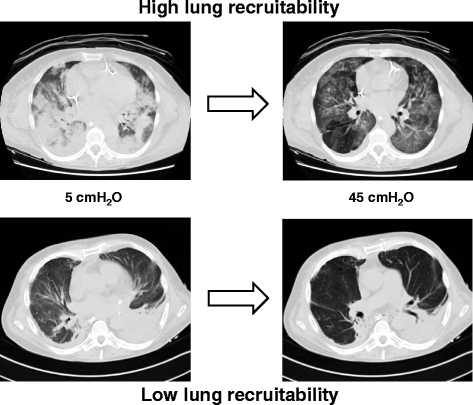
- Caironi P, Carlesso E, Cressoni M, Chiumello D, Moerer O, Chiurazzi C, et al. Lung recruitability is better estimated according to the Berlin definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome at standard 5 cm H2O rather than higher positive end-expiratory pressure: a retrospective cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:781–90. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000770. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

