Nicotine inhibits activation of microglial proton currents via interactions with α7 acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 27256075
- PMCID: PMC5910455
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-016-0460-5
Nicotine inhibits activation of microglial proton currents via interactions with α7 acetylcholine receptors
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Nicotine inhibits activation of microglial proton currents via interactions with α7 acetylcholine receptors.J Physiol Sci. 2018 Nov;68(6):881. doi: 10.1007/s12576-018-0608-6. J Physiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29679307 Free PMC article.
Abstract
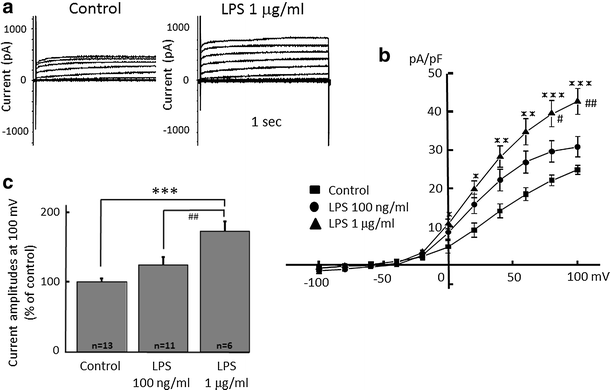
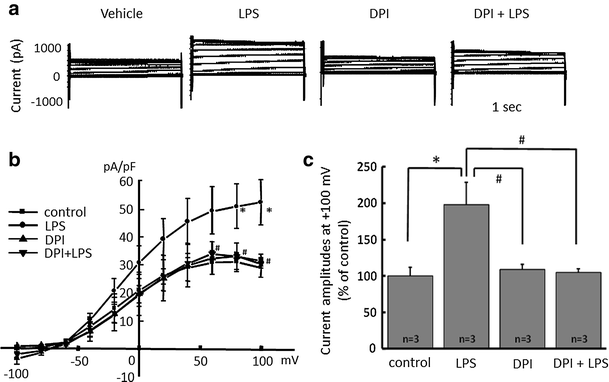
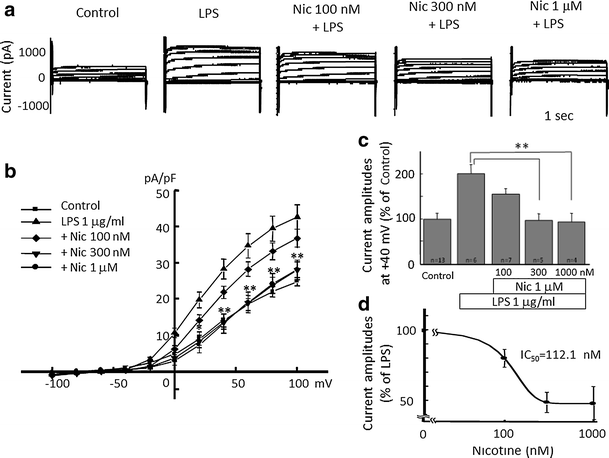
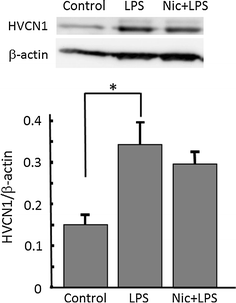
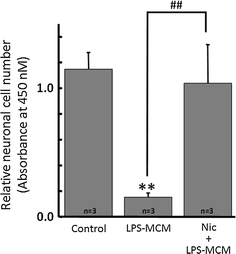
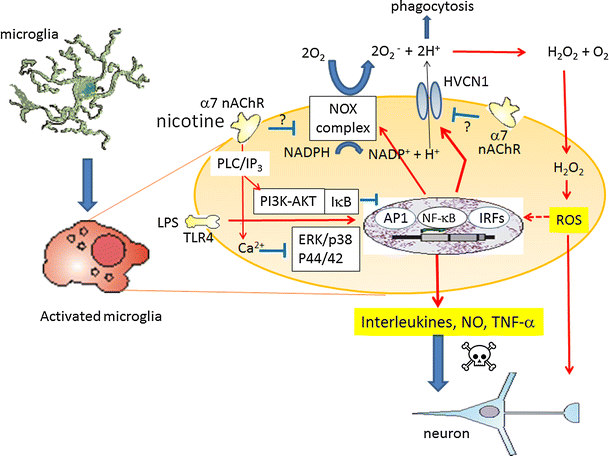
Alpha 7 subunits of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are expressed in microglia and are involved in the suppression of neuroinflammation. Over the past decade, many reports show beneficial effects of nicotine, though little is known about the mechanism. Here we show that nicotine inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced proton (H+) currents and morphological change by using primary cultured microglia. The H+ channel currents were measured by whole-cell patch clamp method under voltage-clamp condition. Increased H+ current in activated microglia was attenuated by blocking NADPH oxidase. The inhibitory effect of nicotine was due to the activation of α7 nAChR, not a direct action on the H+ channels, because the effects of nicotine was cancelled by α7 nAChR antagonists. Neurotoxic effect of LPS-activated microglia due to inflammatory cytokines was also attenuated by pre-treatment of microglia with nicotine. These results suggest that α7 nAChRs in microglia may be a therapeutic target in neuroinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Lipopolysaccharide; Microglia; NADPH oxidase; Nicotine; Proton currents; α7 nAChRs.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microglial alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors drive a phospholipase C/IP3 pathway and modulate the cell activation toward a neuroprotective role.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Jun;83(8):1461-70. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20850. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16652343
-
Primary cultures of rat cortical microglia treated with nicotine increases in the expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (GLAST) via the activation of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 31;258:374-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.044. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24300109
-
Stimulation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates glutamate transporter GLAST via basic fibroblast growth factor production in cultured cortical microglia.Brain Res. 2015 Nov 2;1625:111-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.08.029. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26327163
-
Anti-inflammatory role of microglial alpha7 nAChRs and its role in neuroprotection.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;97(4):463-472. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.07.032. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26232730 Review.
-
Diverse strategies targeting α7 homomeric and α6β2* heteromeric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors for smoking cessation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014 Oct;1327(1):27-45. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12421. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014. PMID: 24730978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a protective effect of the loss of α4-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on Aβ-related neuropathology in Tg2576 mice.Front Neurosci. 2023 Apr 11;17:1097857. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1097857. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37113156 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of spinal alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor shortens the duration of remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia by upregulating KCC2 in the spinal dorsal horn in rats.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan-Dec;13:1744806917704769. doi: 10.1177/1744806917704769. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28425312 Free PMC article.
-
Changing Functional Signatures of Microglia along the Axis of Brain Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1091. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031091. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial cells as therapeutic targets for smoking cessation.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Sep 15;175:108157. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108157. Epub 2020 May 24. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32461156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia morphology and proinflammatory signaling in the nucleus accumbens during nicotine withdrawal.Sci Adv. 2019 Oct 9;5(10):eaax7031. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax7031. eCollection 2019 Oct. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31633029 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

