Open suprapubic versus retropubic prostatectomy in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia during resident's learning curve: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27256183
- PMCID: PMC4871389
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0517
Open suprapubic versus retropubic prostatectomy in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia during resident's learning curve: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Purpose: This study compared the suprapubic (SP) versus retropubic (RP) prostatectomy for the treatment of large prostates and evaluated perioperative surgical morbidity and improvement of urinary symptoms.
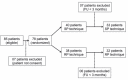
Materials and methods: In this single centre, prospective, randomised study, 65 consecutive patients with LUTS and surgical indication with prostate volume greater than 75g underwent open prostatectomy to compare the RP (32 patients) versus SP (33 patients) technique.
Results: The SP group exhibited a higher incidence of complications (p=0.002). Regarding voiding pattern analysis (IPSS and flowmetry), both were significantly effective compared to pre-treatment baseline. The RP group parameters were significantly better, with higher peak urinary flow (SP: 16.77 versus RP: 23.03mL/s, p=0.008) and a trend of lower IPSS score (SP: 6.67 versus RP 4.14, p=0.06). In a subgroup evaluation of patients with prostate volumes larger than 100g, blood loss was lower in those undergoing SP prostatectomy (p=0.003). Patients with prostates smaller than 100g in the SP group exhibited a higher incidence of low grade late complications (p=0.004).
Conclusions: The SP technique was related to a higher incidence of minor complications in the late postoperative period. High volume prostates were associated with increased bleeding when the RP technique was utilized. The RP prostatectomy was associated with higher peak urinary flow and a trend of a lower IPSS Score.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Comment in
-
Re: Open Suprapubic versus Retropubic Prostatectomy in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia during Resident's Learning Curve: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Urol. 2017 Nov;198(5):955-957. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 29059728 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Bipolar plasma enucleation of the prostate vs open prostatectomy in large benign prostatic hyperplasia cases - a medium term, prospective, randomized comparison.BJU Int. 2013 May;111(5):793-803. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11730.x. Epub 2013 Mar 7. BJU Int. 2013. PMID: 23469933 Clinical Trial.
-
Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic enlargement: surgical technique and outcomes in a high-volume robotic centre.Eur Urol. 2015 Sep;68(3):451-7. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25887786
-
Re: Open Suprapubic versus Retropubic Prostatectomy in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia during Resident's Learning Curve: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Urol. 2017 Nov;198(5):955-957. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 29059728 No abstract available.
-
Prostatectomy for benign prostate disease: open, laparoscopic and robotic techniques.Can J Urol. 2015 Oct;22 Suppl 1:60-6. Can J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26497345 Review.
-
Comparison Between Minimally Invasive Simple Prostatectomy and Open Simple Prostatectomy for Large Prostates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Trials.J Endourol. 2019 Sep;33(9):767-776. doi: 10.1089/end.2019.0306. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Endourol. 2019. PMID: 31244334
Cited by
-
Comparison of Robot-Assisted Versus Open Simple Prostatectomy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Curr Urol Rep. 2018 Jul 12;19(9):71. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0820-1. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29998354 Review.
-
Assessment of Level of Patient Satisfaction after Prostatectomy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Referral Hospitals in Addis Ababa.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020 Sep;30(5):733-738. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v30i5.12. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 33911834 Free PMC article.
-
Same sized three-way indwelling urinary catheters from various manufacturers present different irrigation and drainage properties.Ther Adv Urol. 2020 Jan 9;12:1756287219889496. doi: 10.1177/1756287219889496. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2020. PMID: 31949476 Free PMC article.
-
Benign prostatic hyperplasia surgical treatment trends in the Public Health System in São Paulo, Brazil.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2022 Jun 17;20:eAO6880. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2022AO6880. eCollection 2022. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2022. PMID: 35730806 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic enucleation vs endoscopic vaporization procedures for benign prostatic hyperplasia: how should we choose: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e22882. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022882. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Platz EA, Smit E, Curhan GC, Nyberg LM, Giovannucci E. Prevalence of and racial/ethnic variation in lower urinary tract symptoms and noncancer prostate surgery in U.S. men. Urology. 2002;59:877–883. Erratum in: Urology. 2003;61:1078. - PubMed
-
- Klotz L, Zhang L, Lam A, Nam R, Mamedov A, Loblaw A. Clinical results of long-term follow-up of a large, active surveillance cohort with localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:126–131. - PubMed
-
- Bushman W. Etiology, epidemiology, and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Clin North Am. 2009;36:403–415. - PubMed
-
- AUA Practice Guidelines Committee AUA guideline on management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (2003). Chapter 1: Diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol. 2003;170:530–547. - PubMed
-
- Han MP, Partin AW. Chapter 94, Walsh-Campbell's Urology. 10th ed. Elsevier; 2012. Retropubic and suprapubic open prostatectomy; pp. 2683–2687.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical