Functional characterization of ABCB4 mutations found in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3
- PMID: 27256251
- PMCID: PMC4891722
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26872
Functional characterization of ABCB4 mutations found in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3
Abstract
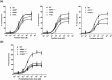
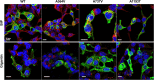
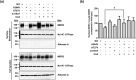
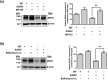
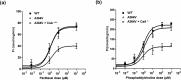
Multidrug resistance 3 (MDR3), encoded by the ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B, member 4 gene (ABCB4), localizes to the canalicular membrane of hepatocytes and translocates phosphatidylcholine from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet of the canalicular membrane. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3) is a rare hepatic disease caused by genetic mutations of ABCB4. In this study, we characterized 8 ABCB4 mutations found in PFIC3 patients, using in vitro molecular assays. First, we examined the transport activity of each mutant by measuring its ATPase activity using paclitaxel or phosphatidylcholine. Then, the pathogenic mechanisms by which these mutations affect MDR3 were examined through immunoblotting, cell surface biotinylation, and immunofluorescence. As a result, three ABCB4 mutants showed significantly reduced transport activity. Among these mutants, one mutation A364V, located in intracellular domains, markedly decreased MDR3 expression on the plasma membrane, while the others did not affect the expression. The expression of MDR3 on the plasma membrane and transport activity of A364V was rescued by a pharmacological chaperone, cyclosporin A. Our study provides the molecular mechanisms of ABCB4 mutations and may contribute to the understanding of PFIC3 pathogenesis and the development of a mutation-specific targeted treatment for PFIC3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A missense mutation in ABCB4 gene involved in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 leads to a folding defect that can be rescued by low temperature.Hepatology. 2009 Apr;49(4):1218-27. doi: 10.1002/hep.22775. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19185004
-
Evaluation of a Novel Missense Mutation in ABCB4 Gene Causing Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 3.Dis Markers. 2020 Jun 15;2020:6292818. doi: 10.1155/2020/6292818. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 32626542 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and structural implications of 25 new ABCB4 mutations in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3).Eur J Hum Genet. 2007 Dec;15(12):1230-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201908. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17726488
-
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep;36 Suppl 1:S26-35. doi: 10.1016/S2210-7401(12)70018-9. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23141890 Review.
-
The spectrum of liver diseases related to ABCB4 gene mutations: pathophysiology and clinical aspects.Semin Liver Dis. 2010 May;30(2):134-46. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1253223. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Semin Liver Dis. 2010. PMID: 20422496 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterisation and Phylogenetic Analysis of 52 Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Genes.Trop Life Sci Res. 2022 Jul;33(2):257-293. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2022.33.2.12. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Trop Life Sci Res. 2022. PMID: 35966264 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic characterization of pediatric patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3): identification of 14 novel ABCB4 variants and review of the literatures.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Dec 22;17(1):445. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02597-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36550572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case report: progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 with compound heterozygous ABCB4 variants diagnosed 15 years after liver transplantation.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Nov 30;21(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-01173-0. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 33256620 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the human lipid exporter ABCB4 in a lipid environment.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;27(1):62-70. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0354-3. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31873305
-
Case series of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3: Characterization of variants in ABCB4 in China.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 8;9:962408. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.962408. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36569137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruetz S. & Gros P. Phosphatidylcholine translocase: a physiological role for the mdr2 gene. Cell 77, 1071–1081 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

