Effects of acute administration of the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen on behavioral flexibility in rats
- PMID: 27256354
- PMCID: PMC4919234
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-016-4321-y
Effects of acute administration of the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen on behavioral flexibility in rats
Abstract
Rationale: The ability to adjust response strategies when faced with changes in the environment is critical for normal adaptive behavior. Such behavioral flexibility is compromised by experimental disruption of cortical GABAergic signaling, as well as in conditions such as schizophrenia and normal aging that are characterized by cortical hyperexcitability. The current studies were designed to determine whether stimulation of GABAergic signaling using the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen can facilitate behavioral flexibility.
Methods: Male Fischer 344 rats were trained in a set-shifting task in which they learned to discriminate between two response levers to obtain a food reward. Correct levers were signaled in accordance with two distinct response rules (rule 1: correct lever signaled by a cue light; rule 2: correct lever signaled by its left/right position). The order of rule presentation varied, but they were always presented sequentially, with the trials and errors to reach criterion performance on the second (set shift) rule providing the measure of behavioral flexibility. Experiments determined the effects of the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen (intraperitoneal, 0, 1.0, 2.5, and 4.0 mg/kg) administered acutely before the shift to the second rule.
Results: Baclofen enhanced set-shifting performance. Control experiments demonstrated that this enhancement was not simply due to improved discrimination learning, nor was it due to impaired recall of the initial discrimination rule.
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that baclofen can facilitate behavioral flexibility, suggesting that GABA(B) receptor agonists may have utility for treating behavioral dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Baclofen; Behavioral flexibility; GABA(B) receptor; Prefrontal cortex; Set shifting.
Figures

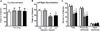


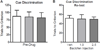
Similar articles
-
Prefrontal cortical GABAergic signaling and impaired behavioral flexibility in aged F344 rats.Neuroscience. 2017 Mar 14;345:274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 26873002 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic interaction between baclofen administration into the median raphe nucleus and inconsequential visual stimuli on investigatory behavior of rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Mar;220(1):15-25. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2450-x. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 21904820 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociable roles for the nucleus accumbens core and shell in regulating set shifting.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 1;26(9):2449-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4431-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16510723 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral analyses of GHB: receptor mechanisms.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Jan;121(1):100-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.10.003. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19010351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACS chemical neuroscience molecule spotlight on STX209 (arbaclofen).ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Aug 17;2(8):381. doi: 10.1021/cn200061g. Epub 2011 Jul 6. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22860166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the rat dorsal medial prefrontal cortex is associated with alcohol-induced cognitive inflexibility.Addict Biol. 2018 Sep;23(5):1117-1129. doi: 10.1111/adb.12568. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Addict Biol. 2018. PMID: 28940879 Free PMC article.
-
In a circuit necessary for cognition and emotional affect, Alzheimer's-like pathology associates with neuroinflammation, cognitive and motivational deficits in the young adult TgF344-AD rat.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Jun 6;39:100798. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100798. eCollection 2024 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39022628 Free PMC article.
-
Decline of prefrontal cortical-mediated executive functions but attenuated delay discounting in aged Fischer 344 × brown Norway hybrid rats.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Dec;60:141-152. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.08.025. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28946018 Free PMC article.
-
Acute vagus nerve stimulation enhances reversal learning in rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021 Oct;184:107498. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107498. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 34332068 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Adenosine Release Is Modulated by NMDA and GABAB Receptors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017 Feb 15;8(2):376-385. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00318. Epub 2017 Jan 30. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28071892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arias C, Mlewski EC, Molina JC, Spear NE. Naloxone and baclofen attenuate ethanol's locomotor-activating effects in preweanling Sprague-Dawley rats. Behav Neurosci. 2009;123:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Arolfo MP, Zanudio MA, Ramirez OA. Baclofen infused in rat hippocampal formation impairs spatial learning. Hippocampus. 1998;8:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Baker KW, Tann B, Mutlu A, Gaebler-Spira D. Improvements in children with cerebral palsy following intrathecal baclofen: use of the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Care and Comfort Caregiver Questionnaire (RIC CareQ) J Child Neurol. 2014;29:312–317. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

