The intercalated nuclear complex of the primate amygdala
- PMID: 27256508
- PMCID: PMC4928580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.05.052
The intercalated nuclear complex of the primate amygdala
Abstract
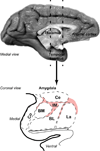
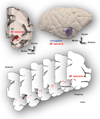
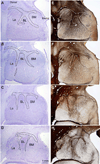
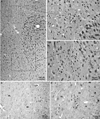
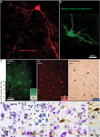
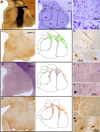
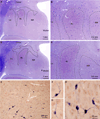
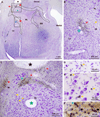
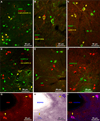
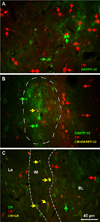
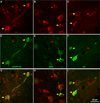
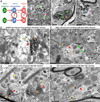
The organization of the inhibitory intercalated cell masses (IM) of the primate amygdala is largely unknown despite their key role in emotional processes. We studied the structural, topographic, neurochemical and intrinsic connectional features of IM neurons in the rhesus monkey brain. We found that the intercalated neurons are not confined to discrete cell clusters, but form a neuronal net that is interposed between the basal nuclei and extends to the dorsally located anterior, central, and medial nuclei of the amygdala. Unlike the IM in rodents, which are prominent in the anterior half of the amygdala, the primate inhibitory net stretched throughout the antero-posterior axis of the amygdala, and was most prominent in the central and posterior extent of the amygdala. There were two morphologic types of intercalated neurons: spiny and aspiny. Spiny neurons were the most abundant; their somata were small or medium size, round or elongated, and their dendritic trees were round or bipolar, depending on location. The aspiny neurons were on average slightly larger and had varicose dendrites with no spines. There were three non-overlapping neurochemical populations of IM neurons, in descending order of abundance: (1) Spiny neurons that were positive for the striatal associated dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32+); (2) Aspiny neurons that expressed the calcium-binding protein calbindin (CB+); and (3) Aspiny neurons that expressed nitric oxide synthase (NOS+). The unique combinations of structural and neurochemical features of the three classes of IM neurons suggest different physiological properties and function. The three types of IM neurons were intermingled and likely interconnected in distinct ways, and were innervated by intrinsic neurons within the amygdala, or by external sources, in pathways that underlie fear conditioning and anxiety.
Keywords: anxiety; connectivity; emotion; inhibition; medium spiny; quantitative anatomy.
Copyright © 2016 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Amaral DG, Price JL, Pitkanen A, Carmichael ST. The Amygdala: neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory, and mental dysfunction. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1992.
-
- Anderson KD, Reiner A. Immunohistochemical localization of DARPP-32 in striatal projection neurons and striatal interneurons: implications for the localization of D1-like dopamine receptors on different types of striatal neurons. Brain Res. 1991;568:235–243. - PubMed
-
- Asan E. Ultrastructural features of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive afferents and their targets in the rat amygdala. Cell Tissue Res. 1997;288:449–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

