Altering Emulsion Stability with Heterogeneous Surface Wettability
- PMID: 27256703
- PMCID: PMC4891714
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26953
Altering Emulsion Stability with Heterogeneous Surface Wettability
Abstract
Emulsions-liquid droplets dispersed in another immiscible liquid-are widely used in a broad spectrum of applications, including food, personal care, agrochemical, and pharmaceutical products. Emulsions are also commonly present in natural crude oil, hampering the production and quality of petroleum fuels. The stability of emulsions plays a crucial role in their applications, but controlling the stability without external driving forces has been proven to be difficult. Here we show how heterogeneous surface wettability can alter the stability and dynamics of oil-in-water emulsions, generated by a co-flow microfluidic device. We designed a useful methodology that can modify a micro-capillary of desired heterogeneous wettability (e.g., alternating hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions) without changing the hydraulic diameter. We subsequently investigated the effects of flow rates and heterogeneous wettability on the emulsion morphology and motion. The experimental data revealed a universal critical timescale of advective emulsions, above which the microfluidic emulsions remain stable and intact, whereas below they become adhesive or inverse. A simple theoretical model based on a force balance can be used to explain this critical transition of emulsion dynamics, depending on the droplet size and the Capillary number-the ratio of viscous to surface effects. These results give insight into how to control the stability and dynamics of emulsions in microfluidics with flow velocity and different wettability.
Figures

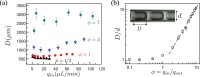
 ), ϕ = 3 (
), ϕ = 3 ( ), ϕ = 7 (
), ϕ = 7 ( ). (b) Effect of flow ratio on the dimensionless droplet length D, normalized with the capillary diameter, d. The dashed line is the best fit of the power-law relation: D/d ~ ϕ10/9.
). (b) Effect of flow ratio on the dimensionless droplet length D, normalized with the capillary diameter, d. The dashed line is the best fit of the power-law relation: D/d ~ ϕ10/9.
 , ■), (iii) inversion of oil droplets to become water-in-oil emulsions (▼), and (iv) break-up of the oil droplets with unstable lubrication films (Δ, ∇, ●). See Supplementary information for the details.
, ■), (iii) inversion of oil droplets to become water-in-oil emulsions (▼), and (iv) break-up of the oil droplets with unstable lubrication films (Δ, ∇, ●). See Supplementary information for the details.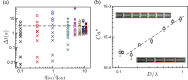
Similar articles
-
Monodisperse Micro-Oil Droplets Stabilized by Polymerizable Phospholipid Coatings as Potential Drug Carriers.Langmuir. 2015 Sep 15;31(36):9762-70. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b02747. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Langmuir. 2015. PMID: 26303989
-
In-Channel Responsive Surface Wettability for Reversible and Multiform Emulsion Droplet Preparation and Applications.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 May 8;11(18):16934-16943. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b03160. Epub 2019 Apr 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30983312
-
Magnetically recoverable poly (methyl methacrylate-acrylic acid)/iron oxide magnetic composites nanomaterials with hydrophilic wettability for efficient oil-water separation.J Environ Manage. 2022 Oct 1;319:115690. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115690. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Environ Manage. 2022. PMID: 35834853
-
Microfluidics as a tool to assess and induce emulsion destabilization.Soft Matter. 2022 Jan 26;18(4):698-710. doi: 10.1039/d1sm01588e. Soft Matter. 2022. PMID: 35037925 Review.
-
Robust bioinspired surfaces and their exploitation for petroleum hydrocarbon remediation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Sep;29(41):61881-61895. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16525-3. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34545517 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic production of monodisperse emulsions for cosmetics.Biomicrofluidics. 2021 Oct 26;15(5):051302. doi: 10.1063/5.0057733. eCollection 2021 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2021. PMID: 34733378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schramm L. L. Emulsions, Foams, and Suspensions: Fundamentals and Applications (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005).
-
- Muschiolik G. Multiple emulsions for food use. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 12, 213–220 (2007).
-
- Taylor K. C. & Hawkins B. F. Emulsions in Enhanced Oil Recovery. vol. 231 (1992).
-
- Dams S. S. & Walker I. M. Multiple emulsions as targetable delivery systems. Methods Enzymol. 149, 51–64 (1987). - PubMed
-
- Nakano M. Places of emulsions in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 45, 1–4 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

